Atlas of War by NatGeo
Ref: National Geographic (2020). Atlas of War.
__________________________________________________________________________________
Summary
An exceptionally well-done summary of influential conflicts throughout world history.
__________________________________________________________________________________
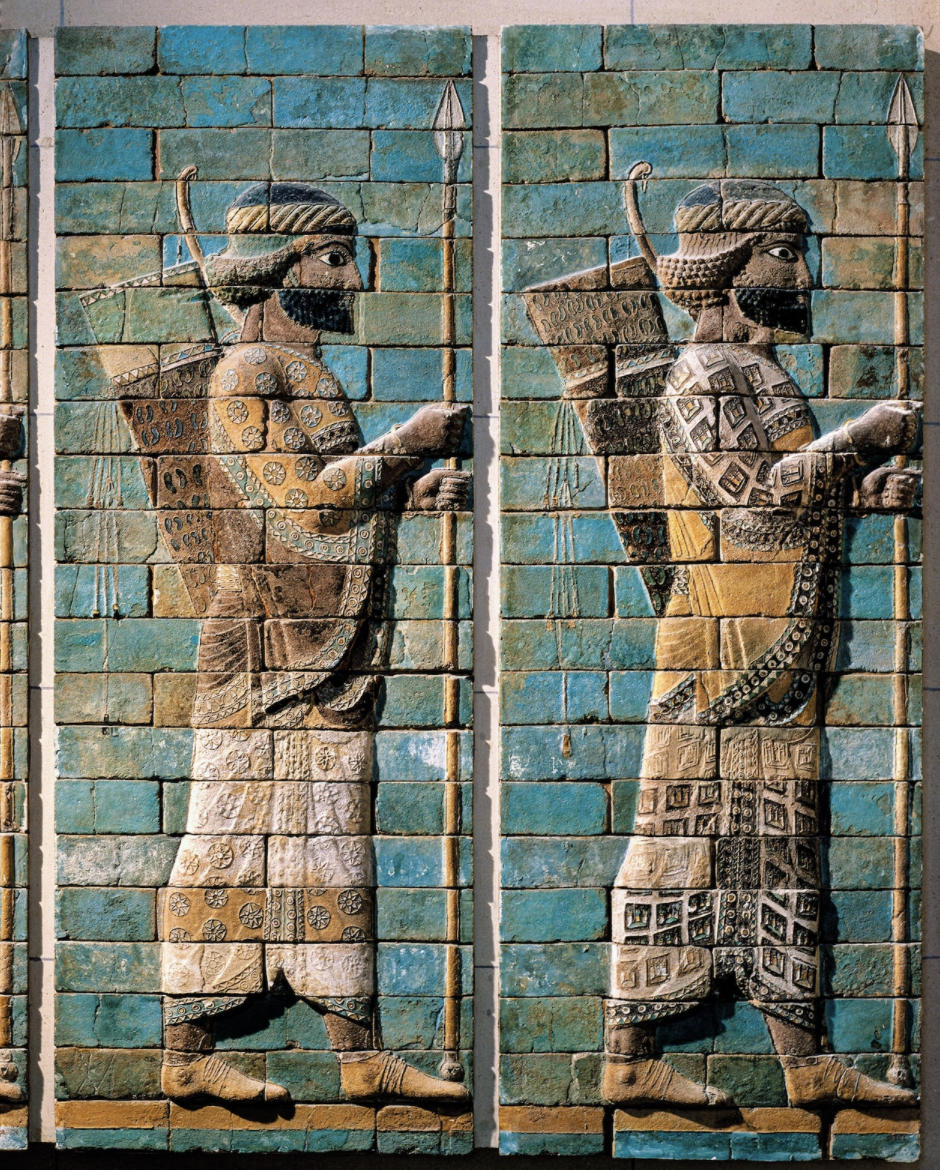
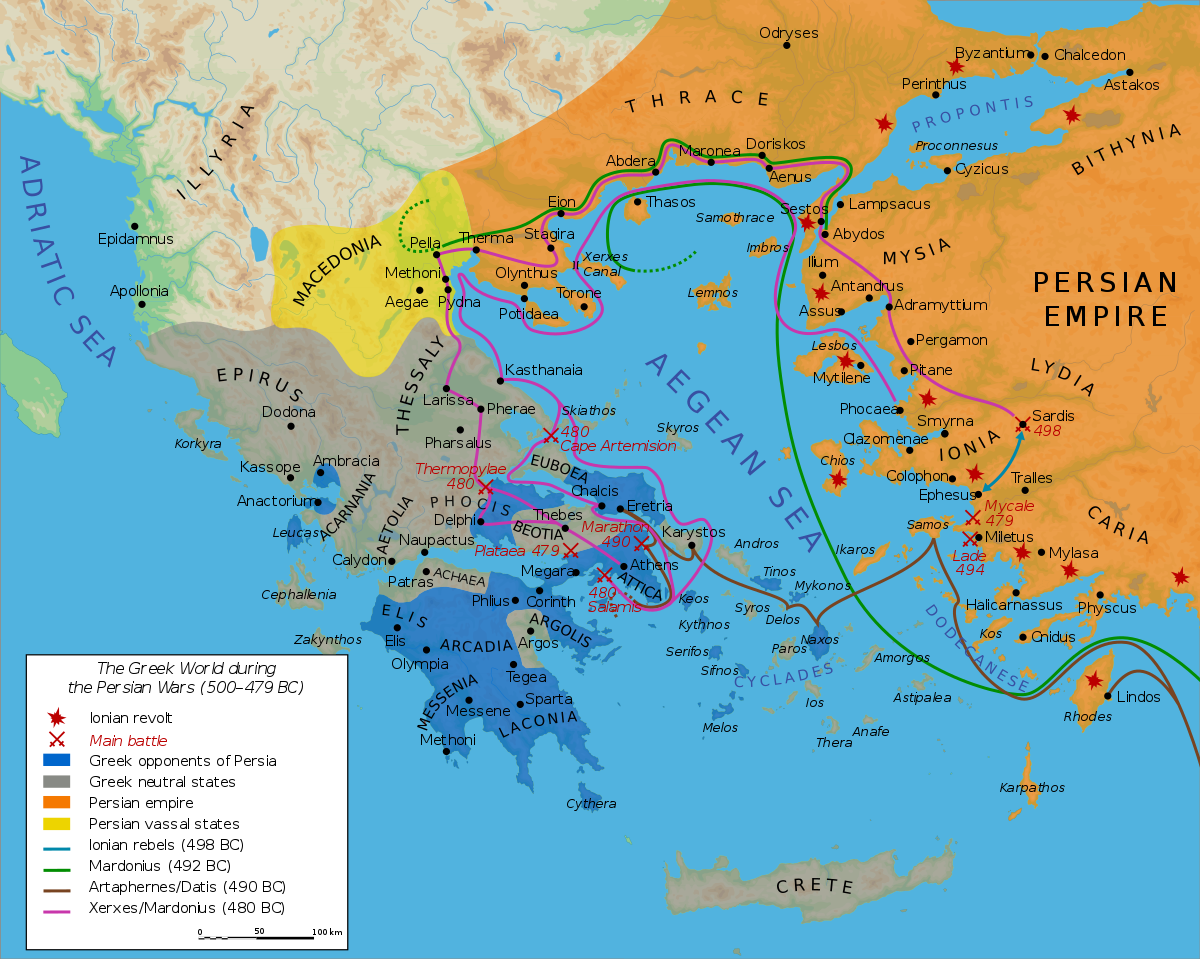
Greco-Persian Wars
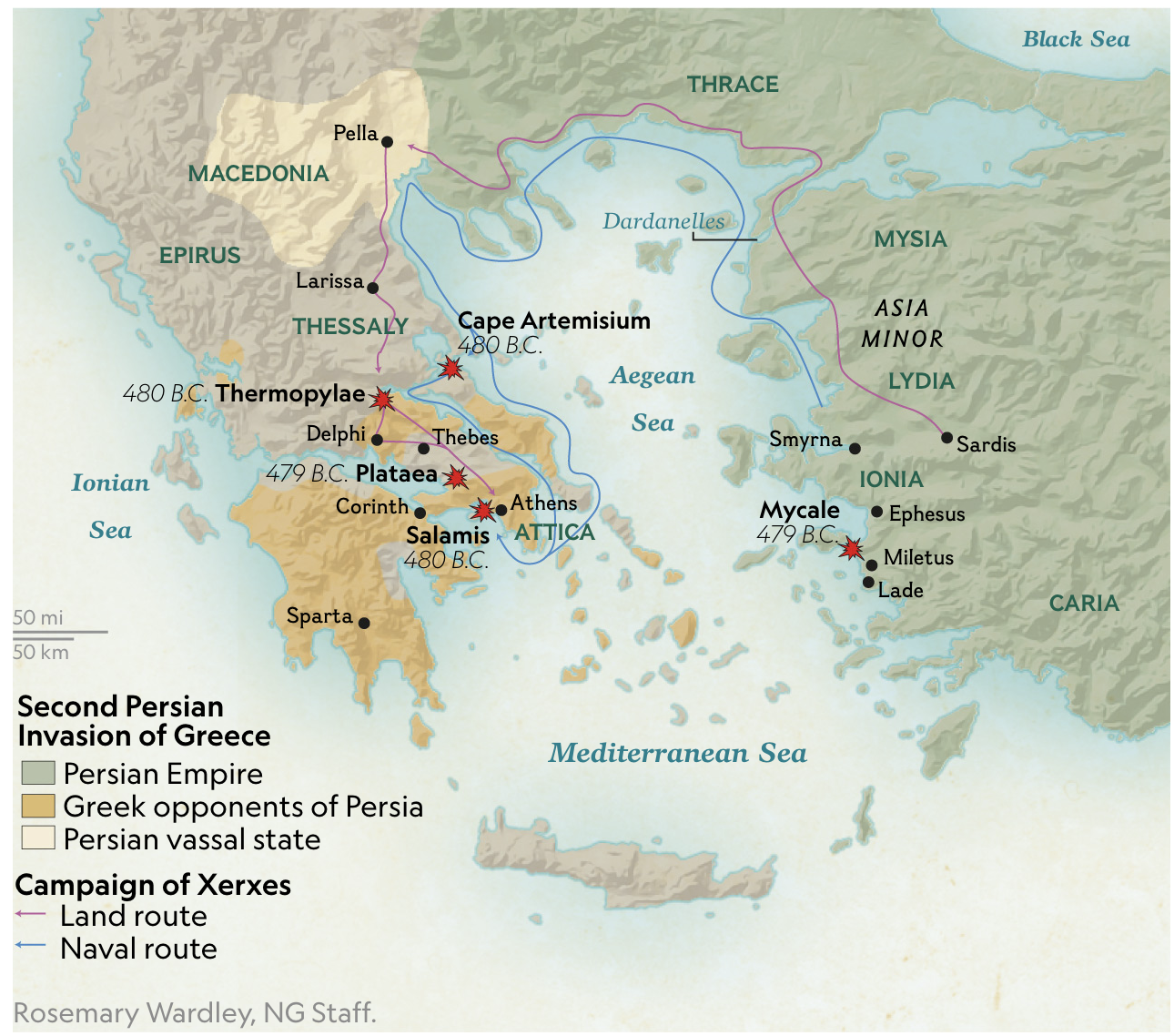
479 BCE: The Battle of Platea; Greek forces rout the Persians on land at Plataea and at sea at Mycale, ending the first Greco-Persian War.-War by NatGeo.
Sep, 480 BCE: The Battle of Salamis; the Greeks defeat Persians in a decisive naval battle near the island of Salamis. Greek Commander Themistocles tricked the Persians in a feigned retreat drawing Persian triremes into an exposed position vulnerable to attack. The Greeks lost only 40 vessels to the Persians 300.-War by NatGeo.
Aug, 480 BCE: The Persians take an abandoned Athens, sacking and burning the city.-War by NatGeo.
Aug, 480 BCE: The Battle of Thermopylae; Persian forces defeat a heavily outnumbered Greek force led by Spartan King Leonidas, at the pass of Thermopylae. Seeing the end approaching, Leonidas ordered all soldiers except his 300 Spartans and a handful of others to retreat. Standing alone at the pass, they died to the last man.-War by NatGeo.
481 BCE: Persian Emperor Xerxes I begins a new invasion of Greece, marching through Thrace, with some 75,000 soldiers supported by a Navy.-War by NatGeo.
480’s BCE: Formation of the Hellenic League by squabbling Greek city-states in anticipation of a follow-on Persian Invasion.-War by NatGeo.
Sep, 490 BCE: The Battle of Marathon; outnumbered Athenian soldiers defeat the invading Persians at Marathon. Prior to battle, the Athenians called upon Sparta for aid but were turned down, as the Spartans were observing a religious holiday. With 10K Athenian soldiers and 1K allies from Platea, the Athenian general Miltiades made a bold decision: Attack the Persian lines head-on at a run. Charging forward in heavy armor, the Athenians surprised their opponents and crushed them at close quarters.-War by NatGeo.
Summer, 490 BCE: Darius deploys 600 ships and some 25K soldiers under Median Admiral Datis, across the Aegean to the city of Eretria. Besieged, Eretria quickly surrenders. The Persians move on to the plain of Marathon, some 39km North of Athens.-War by NatGeo.
491 BCE: Persian Emperor Darius I sends envoys to Athens and Sparta asking for a tribute of earth and water, symbols of submission. The Athenians threw the heralds into a pit; the Spartans hurled theirs into a well and told them to take their land and water from there.-War by NatGeo.
493 BCE: Persian forces take back the Ionian cities and begin to plan for an attack on Athens.-War by NatGeo.
499 BCE: Greek cities in Ionia (Asia Minor) with the support of Athens rebel against Persian Rule.-War by NatGeo.
__________________________________________________________________________________
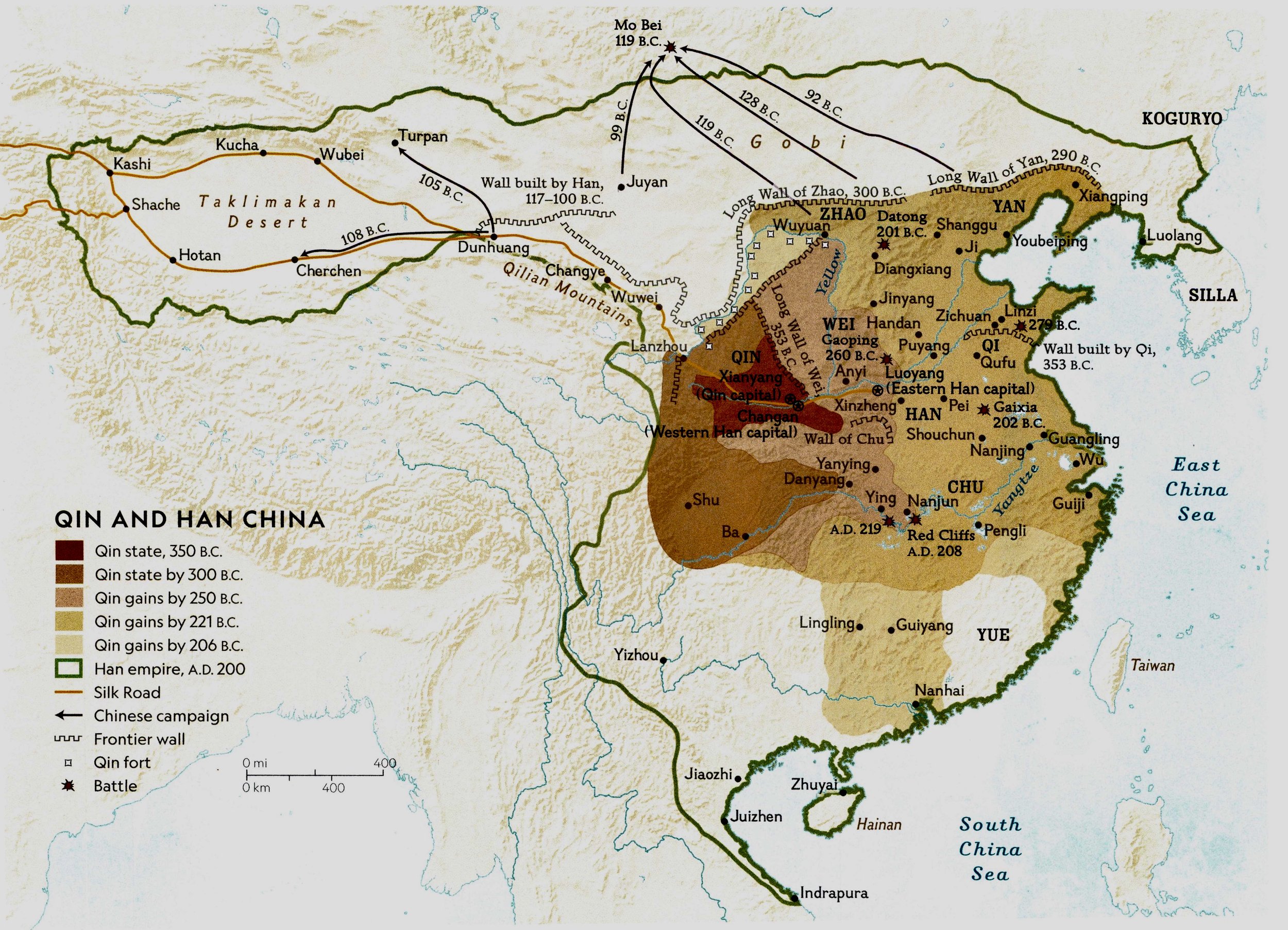
China’s Warring States
475-221 BCE: China’s Warring States Period.-War by NatGeo.
221 BCE: The Chinese Qin ruler, King Zhao Zheng becomes Emperor Qin Shi Huang Di and rules as the first Chinese Emperor of unified China.-War by NatGeo.
246 BCE: Zhao Zheng gains the throne of the Chinese state of Qin at the age of 13.-War by NatGeo.
256 BCE: Conquest of the Chinese state of Qin ends the power of the Eastern Zhou dynasty.-War by NatGeo.
260 BCE: The Battle of Changping; the Chinese state of Qin defeats the state of Zhao. Trapped against Qin fortifications, the Zhao army starved. After 46 days, Zhao Kuo tried one last time to break out and was killed by enemy arrows. The rest of the Army- reportedly 400K- surrendered to the Qin. All were executed save 240 men.-War by NatGeo.
278 BCE: The Chinese state of Qin conquers the state of Chu.-War by NatGeo.
338 BCE: Execution of Qin administrator Shang Yang; reportedly tied to four chariots and driven off in different directions.-War by NatGeo.
340 BCE: The Chinese state of Qin attacks and subdues the state of Wei, which had been weakened by previous attacks from its neighbor Han.-War by NatGeo.
361 BCE: Shang Yang takes over as administrator of the Chinese state of Qin.-War by NatGeo.
375 BCE: The Chinese state of Han conquers the central minor state of Zheng.-War by NatGeo.
~400 BCE: Most of China’s quarreling states consolidate into 7 major powers: Qin, Qi, Chu, Yan, Han, Wei, and Zhao.-War by NatGeo.
403 BCE: The Chinese states of Wei, Zhao, and Han are formed from the old Jin territory.-War by NatGeo.
__________________________________________________________________________________
Alexander the Great
323 BCE: Death of Alexander of Macedonia in Babylon at the age of 32.-War by NatGeo.
324 BCE: Alexander’s troops rebel against further exploration. Alexander turns back toward Mesopotamia.-War by NatGeo.
327 BCE: Alexander’s troops begin their march to India. Alexander marries Roxana, daughter of a Bactrian chief.-War by NatGeo.
334 BCE: Invasion of the Persian Empire by Macedonian forces under Alexander.-War by NatGeo.
330 BCE: Sack of Persepolis by Alexander’s forces. Darius III is killed by his own men.-War by NatGeo.
331 BCE: Battle of Gaugamela; Alexander defeats Darius III near the town of Gaugamela (present day Iraq); After a strategic delay, Alexander led his cavalry across the Persian left flank, through a gap, and turned it against the Persian center. Again, Darius III fled, and Alexander’s Army took the day.-War by NatGeo.
333 BCE: Battle of Issus; Alexander defeats Persian King Darius III; Alexander had left sick soldiers in Issus to recover. Persian King Darius III swept in behind him and massacred the troops left behind. Alexander then reversed course and met Darius on the coast plain near Issus. Darius fielded more than 100,000 soldiers including cavalry and infantry against Alexanders 40,000 or so troops. Alexander left the elite cavalry corps known as the Companions at the center while charging towards the Persian left wing, Alexanders cavalry broke through the enemy lines and attacked the Persian center. Terrified, Darius III fled the battlefield, leaving behind not only his weapons and cloak, but also his wife, mother, and children.-War by NatGeo.
334 BCE: Battle of the Granicus; Alexander wins his first big battle against the Persians at the Granicus River.-War by NatGeo.
336 BCE: Assassination of King Phillip of Macedon. His son Alexander assumes the throne.-War by NatGeo.
__________________________________________________________________________________
Punic Wars
410: Fall of the Western Roman Empire; Visigoth’s invade and sack Rome.-War by NatGeo.
10: Roman expansion is forced to a halt at the Rhine and Danube Rivers, where a long line of forts and watchtowers mark the limits of Rome’s power.-War by NatGeo.
9: German chieftain Arminius, leader of the Cherusci tribe and a supposed Roman ally deceives Roman Governor Varus telling him that certain other tribes were rising up in rebellion to the NW. Varus marched out with three legions to subdue the supposed rebels and found himself surrounded on all sides. After 4 days of fighting, all 3 legions, 20,000 Romans, were killed.-War by NatGeo.
50s BCE: Battle of Teutoburg Forest; Roman forces under Julius Caesar defeat Gallic tribes.-War by NatGeo.
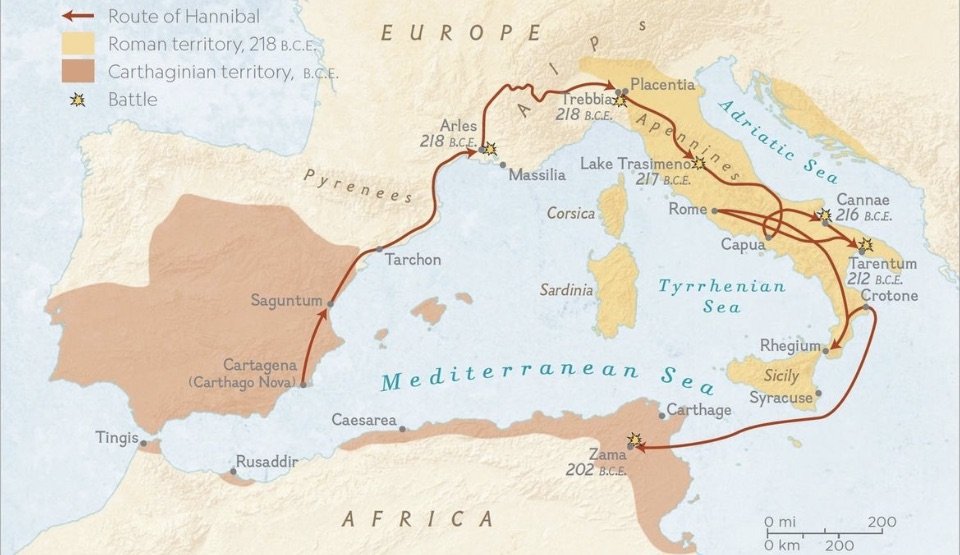
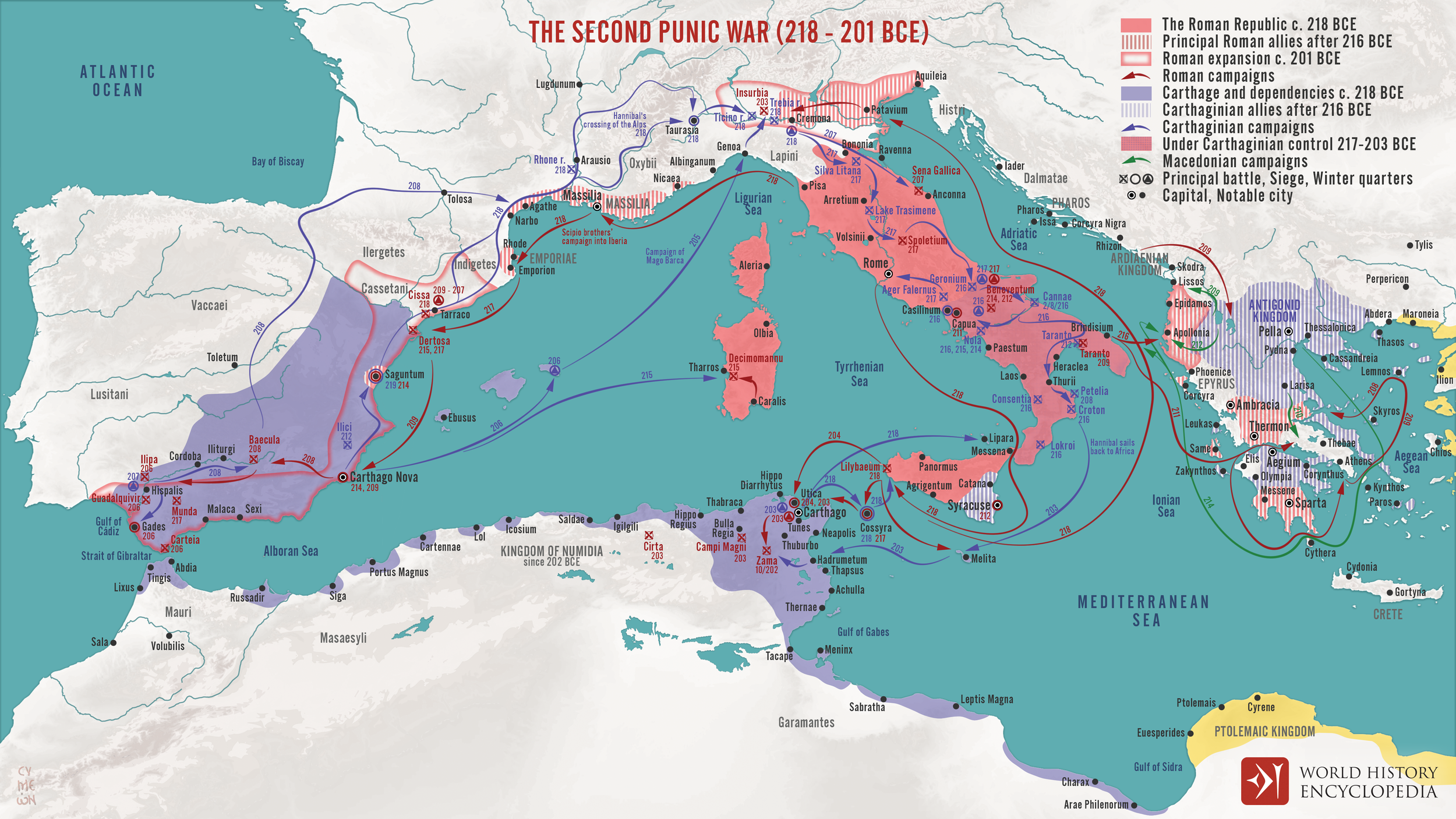
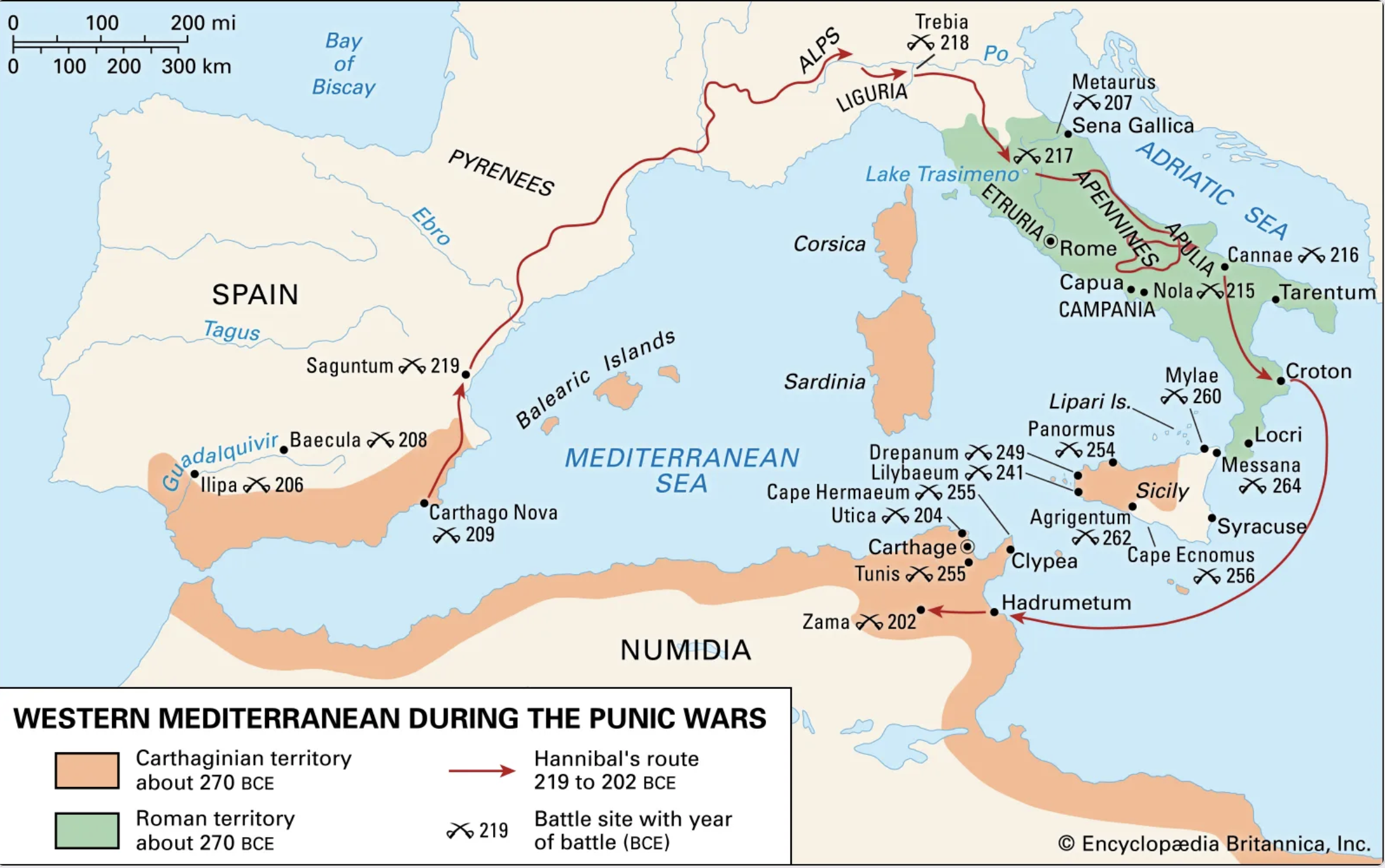
264-146 BCE: The Punic Wars; Rome defeats Carthage (so-called because the Romans knew the Carthaginians as Poeni).-War by NatGeo.
149-146 BCE: Third Punic War; Roman forces under Scipio Aemilianus (grandson of Scipio Africanus) besieges, destroys, and razes the City of Carthage (to which Scipio is said to have wept at the sight).-War by NatGeo.
218-202 BCE: Second Punic War; Carthage marches on Rome and wins key battles, but Roman troops eventually win back land and defeat Carthage at the Battle of Zama in Tunisia.-War by NatGeo.
202 BCE: The Battle of Zama; Rome forces under Scipio Africanus defeat Carthaginian forces under Hannibal in Zama, Tunisia, ending the 2nd Punic War.-War by NatGeo.
209 BCE: The Second Battle of Tarentum; Roman forces led by Quintus Fabius Maximus Verrucosus recapture the city of Tarentum, that had betrayed them in the first Battle of Tarentum (Wiki).
212 BCE: The First Battle of Tarentum; Carthaginian forces under Hannibal capture the Roman city of Tarentum, killing only Romans (Wiki).
216 BCE: The Battle of Cannae; Hannibal’s forces defeat Rome near the fortress of Cannae. Hannibal shaped his troops into an unconventional formation, with the weakest spot in the middle and the strongest forces on the flanks. As the Romans charged, the Carthaginian center fell back while their stronger infantry and cavalry swung around and enveloped the Romans on either side. The result was a massacre, with some 50K-70K Roman soldiers killed as they fought or tried to flee.-War by NatGeo.
21 Jun, 217 BCE: The Battle of Lake Trasimeno; Carthaginian forces under Hannibal ambush Roman forces under Gaius Flaminius on the N. shore of Lake Trasimene, resulting in a heavy defeat for the Romans (Wiki).
22 Dec, 218 BCE: The Battle of Trebbia; the first major battle of the 2nd Punic War. Carthaginian forces under Hannibal defeat Roman forces under Sempronius Longus, resulting in a heavy defeat for the Romans (Wiki).
264-261 BCE: First Punic War; Rome defeats Carthage at sea after territorial disputes over the island of Sicily. Rome then annexes Corsica and Sardinia.-War by NatGeo.
247-183 BCE: Life of Hannibal Barca, who poisoned himself in a fortress surrounded by enemies.-War by NatGeo.
300 BCE: Roman soldiers begin to be paid a regular stipend.-War by NatGeo.
509 BCE: According to traditional accounts, Roman King Tarquin is overthrown to end the Roman Monarchy.-War by NatGeo.
753 BCE: According to legend, Romulus and Remus establish the first Roman Kingdom.-War by NatGeo.
__________________________________________________________________________________
The Norman Conquest
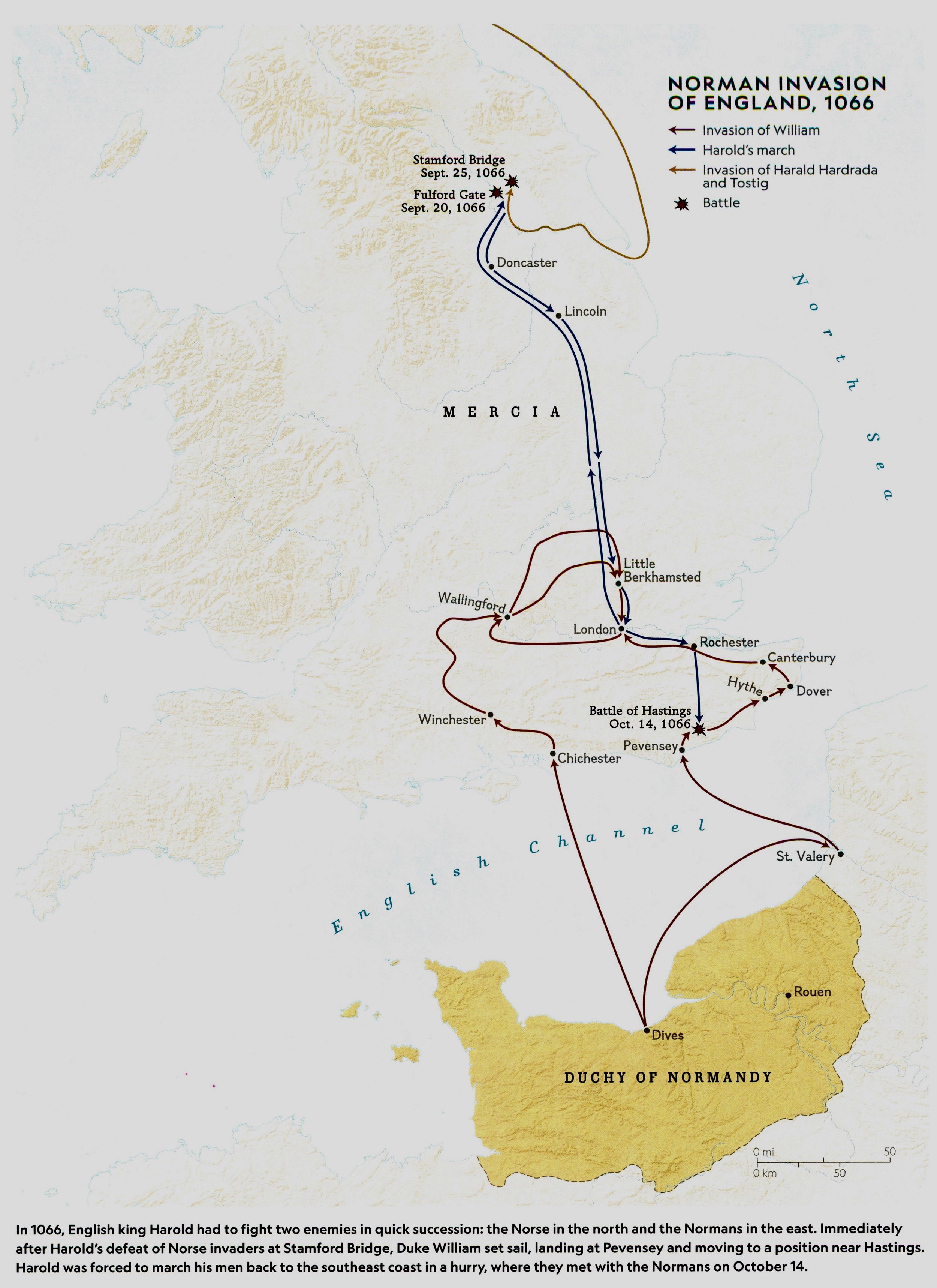
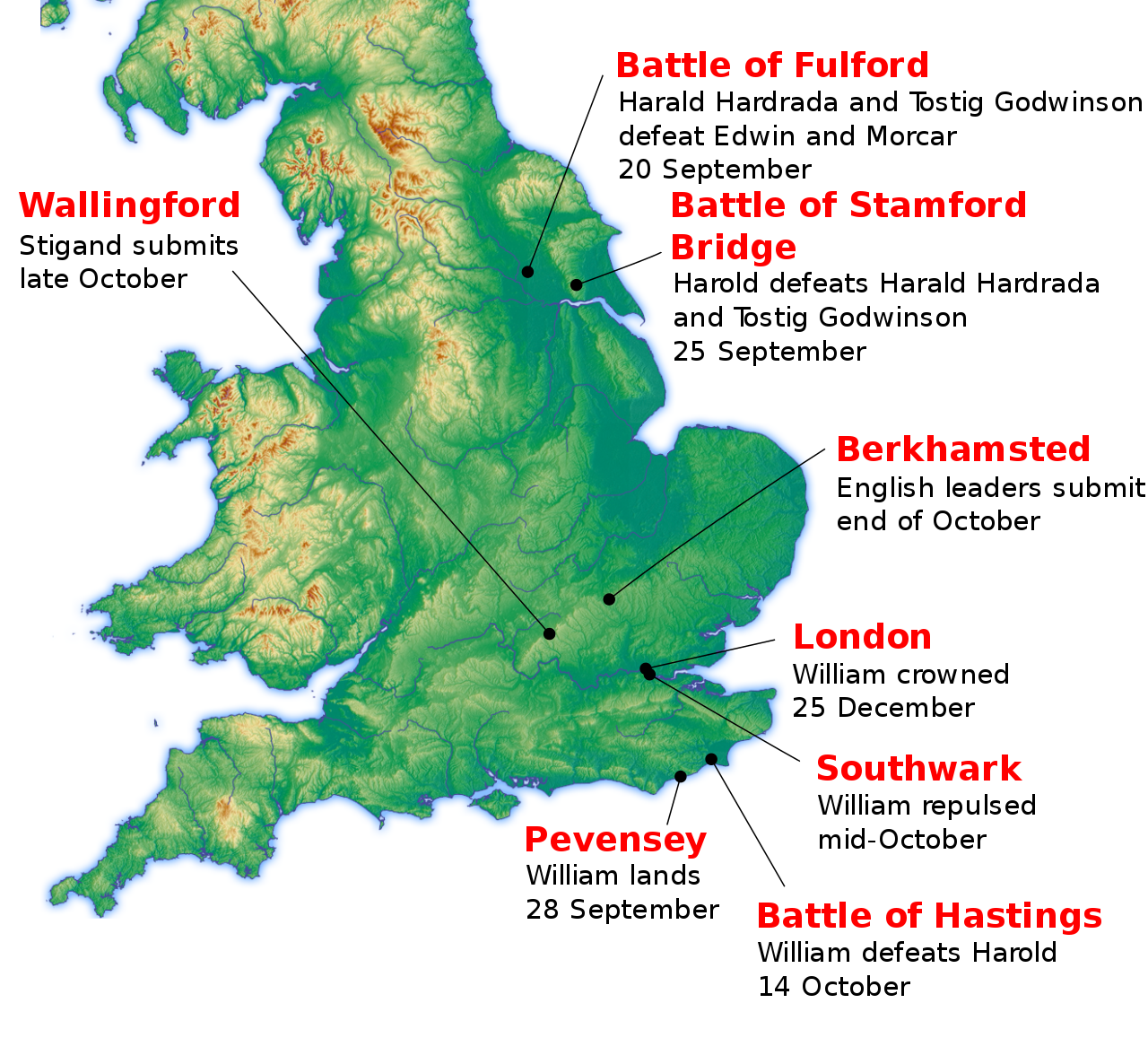
25 Dec, 1066: William of Normandy becomes William I, King of England.-War by NatGeo.
14 Oct, 1066: Battle of Hastings; Norman armies defeat the English. Harold took up position on the hill of Senlac, near the town of Hastings. Norman archers showered the English with arrows; the English shield wall held them back. Eventually, Norman forces wore down the axe-wielding English, and Harold himself was killed, apparently by an arrow through the eye. By the end of the day, the Normans had won.-War by NatGeo.
28 Sep, 1066: Duke William and his Army land in Pevensey in England.-War by NatGeo.
25 Sep, 1066: Battle of Yorkshire; English forces under King Harold defeats invading Norsemen in Yorkshire; Harold faced a new threat, his brother and bitter enemy Tostig had joined forces with Harald Hardrada, king of Norway, to invade the North of Britain. Harold marched his soldiers at speed to York to meet the invaders. At one point the English advance was supposedly held off by a single Viking, who reputedly killed 40 enemies defending Stamford Bridge until an English soldier who floated under the bridge stabbed him through a chink in the planks. Harold then hustles his troops down to Southern England to meet William’s Army.-War by NatGeo.
20 Sep, 1066: The Battle of Fulford Gate; Norwegian forces under Norwegian King Harald III (‘Harald Hardrada’) and his English ally Tostig Godwinson defeat Northern Earls Edwin and Morcar, gaining Fulford and later York.-War by NatGeo.
Apr, 1066: Halley’s comet appears in the skies and is seen as a bad omen for England.-War by NatGeo.
5 Jan, 1066: Death of English Kish Edward the Confessor. The Witan, the council of Anglo-Saxon leaders, names Harold Godwinson King.-War by NatGeo.
1064: Harold Godwinson is shipwrecked in Normandy; According to Norman accounts- Harold swears an oath to uphold William’s claim to the English throne.-War by NatGeo.
1042: Edward the Confessor becomes King of England (according to Normal claim- Edward promised William to be his heir).-War by NatGeo.
1035: William the Bastard (cousin to English King Edward the Confessor) becomes duke of Normandy.-War by NatGeo.
__________________________________________________________________________________
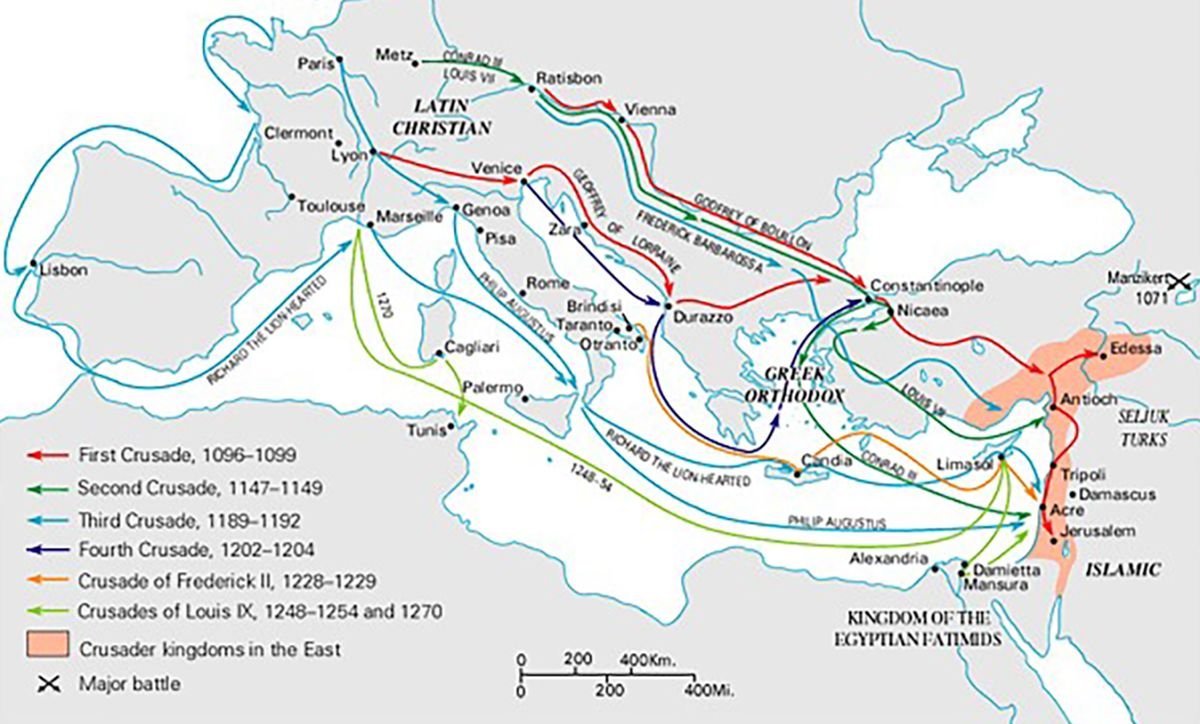
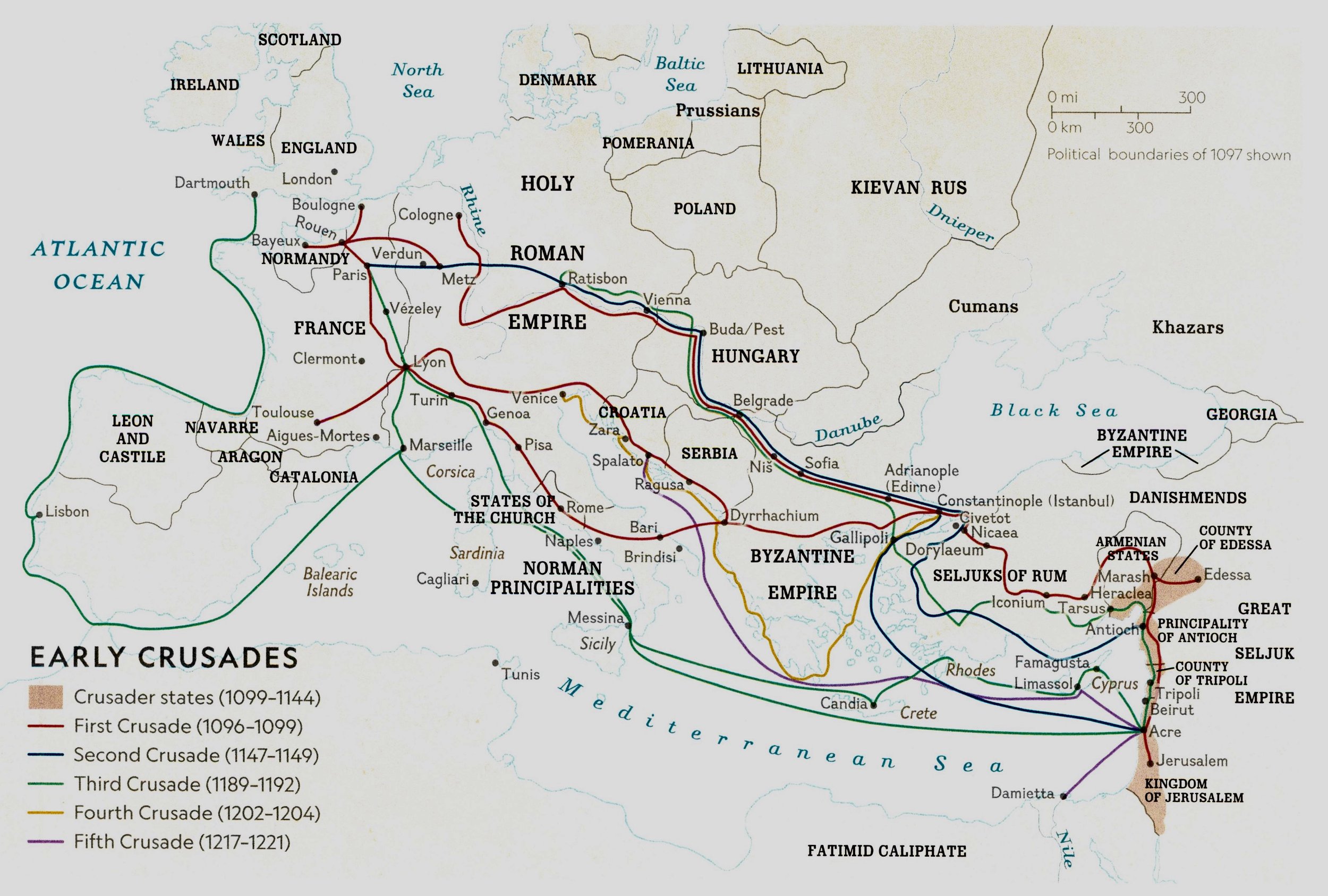
The Holy Wars
1096-1272: The Crusades are fought between European Christians and Middle Eastern Muslims.-War by NatGeo.
1270-1272: Eighth Crusade; King Louis again leads a crusade but dies upon reaching Africa. His army returns to Europe.-War by NatGeo.
1248-1254: Seventh Crusade; King Louis IX of France briefly captures Damietta in Egypt before being captured and ransomed himself, forcing the surrender of Damietta.-War by NatGeo.
1228-1229: Sixth Crusade; Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II temporarily regains Jerusalem.-War by NatGeo.
1217-1221: Fifth Crusade; Crusaders attempt to take Egypt but fail.-War by NatGeo.
1202-1204: Fourth Crusade; Crusaders place Baldwin of Flanders on the throne in Constantinople.-War by NatGeo.
1189- 1192: Third Crusade; Richard I (Lionheart), Frederick I (Barbarossa), and other leaders retake Acre and other coastal cities.-War by NatGeo.
2 Oct, 1187: Fall of Jerusalem; Saladin and his Muslim Army retake the city of Jerusalem.-War by NatGeo.
1187: Battle on the Horns of Hattin; Muslim leader Saladin retakes crusader-occupied cities; Saladin had united several Muslim territories in the 1170’s and 1180’s. In 1187 after a Christian leader broke a truce, Saladin declared war and besieged the crusader city of Tiberias near the Sea of Galilee. Jerusalem’s King Guy marched his 20,000 soldiers across the desert and was defeated by Saladin’s army, 30,000 strong. Saladin reconquers Acre, Ascalon, and then proceeds to Jerusalem.-War by NatGeo.
1147-1149: Second Crusade; Louis VII of France, Conrad III of Germany, and Baldwin III of Jerusalem attempt to take Damascus but fail.-War by NatGeo.
1096-1099: First Crusade; Crusaders take Jerusalem and establish Crusader States.-War by NatGeo.
15 Jul, 1099: Fall of Jerusalem; Crusaders defeat the Turks and take the city.-War by NatGeo.
1099: Battle of Jerusalem; the Crusaders reach Jerusalem with only 1500 mounted men and 12,000 infantry. Jerusalem’s governor had poisoned the wells around the city. Relief arrived in the form of 6 European Ships. Using scavenged wood and the timber of the ship’s themselves, the crusaders built ladders, catapults, and siege towers, retaking the city.-War by NatGeo.
1098: Fall of Antioch; the Crusader Bohemond bribes a Turkish guard into admitting them over the walls, Europeans pour into the city, capturing Antioch.-War by NatGeo.
1097: Battle of Antioch; Crusaders advance into Anatolia and are reduced to eating dogs, rats, and even seeds picked out of manure in the parched lands.-War by NatGeo.
1095: The Council of Clermont; Pope Urban II issues a challenge- Western warriors should take up the cross, become soldiers of god, and reclaim the Holy Land from the Muslims. Struggling to control their unruly flocks, the Catholic Church under Pope Gregory VII and his successor, Pope Urban II, decide to divert popular energies to a useful goal- retaking Jerusalem and the lands around it.-War by NatGeo.
1071: Christian Territories including Jerusalem are captured by Seljuk Turks.-War by NatGeo.
__________________________________________________________________________________
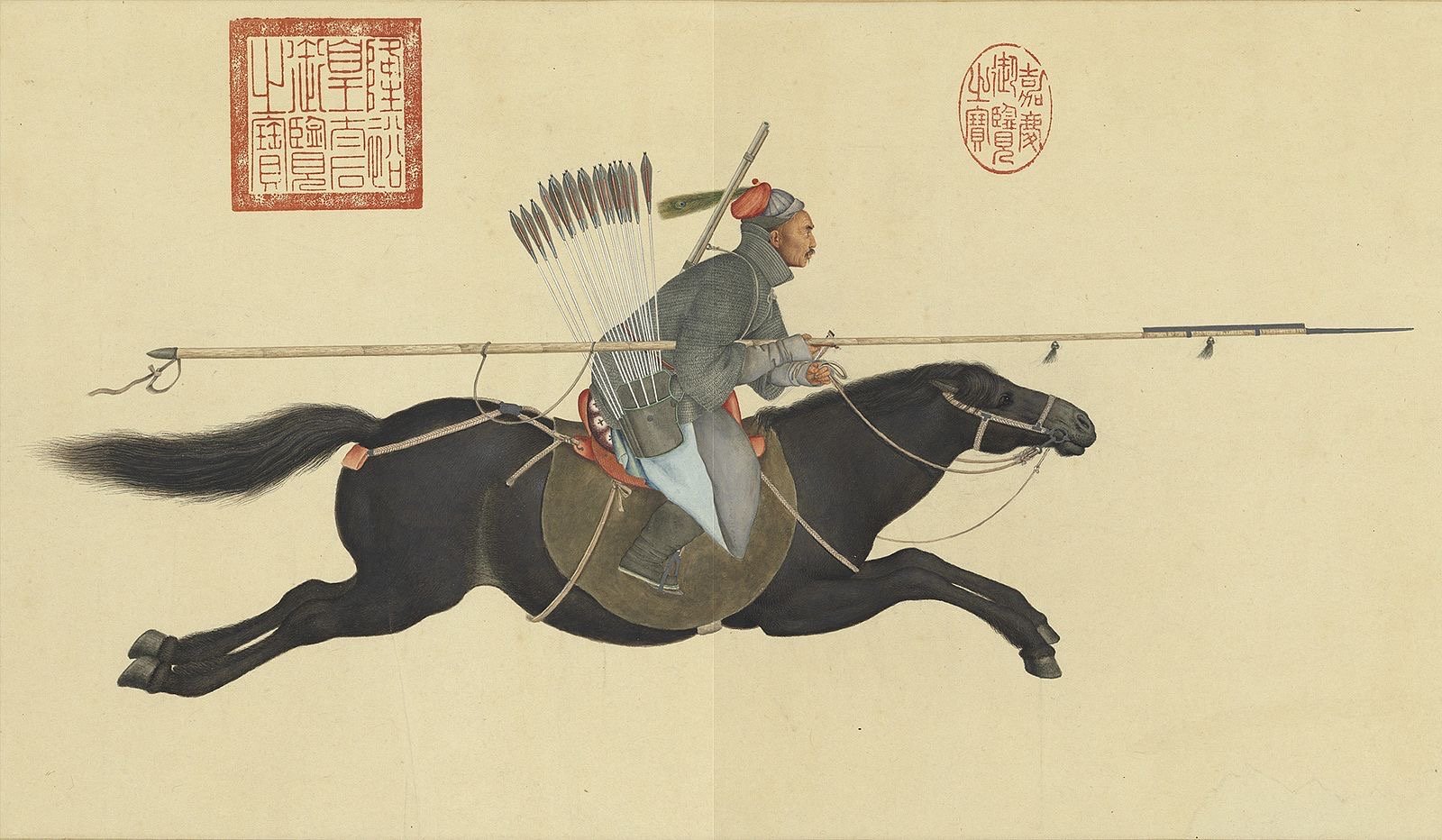
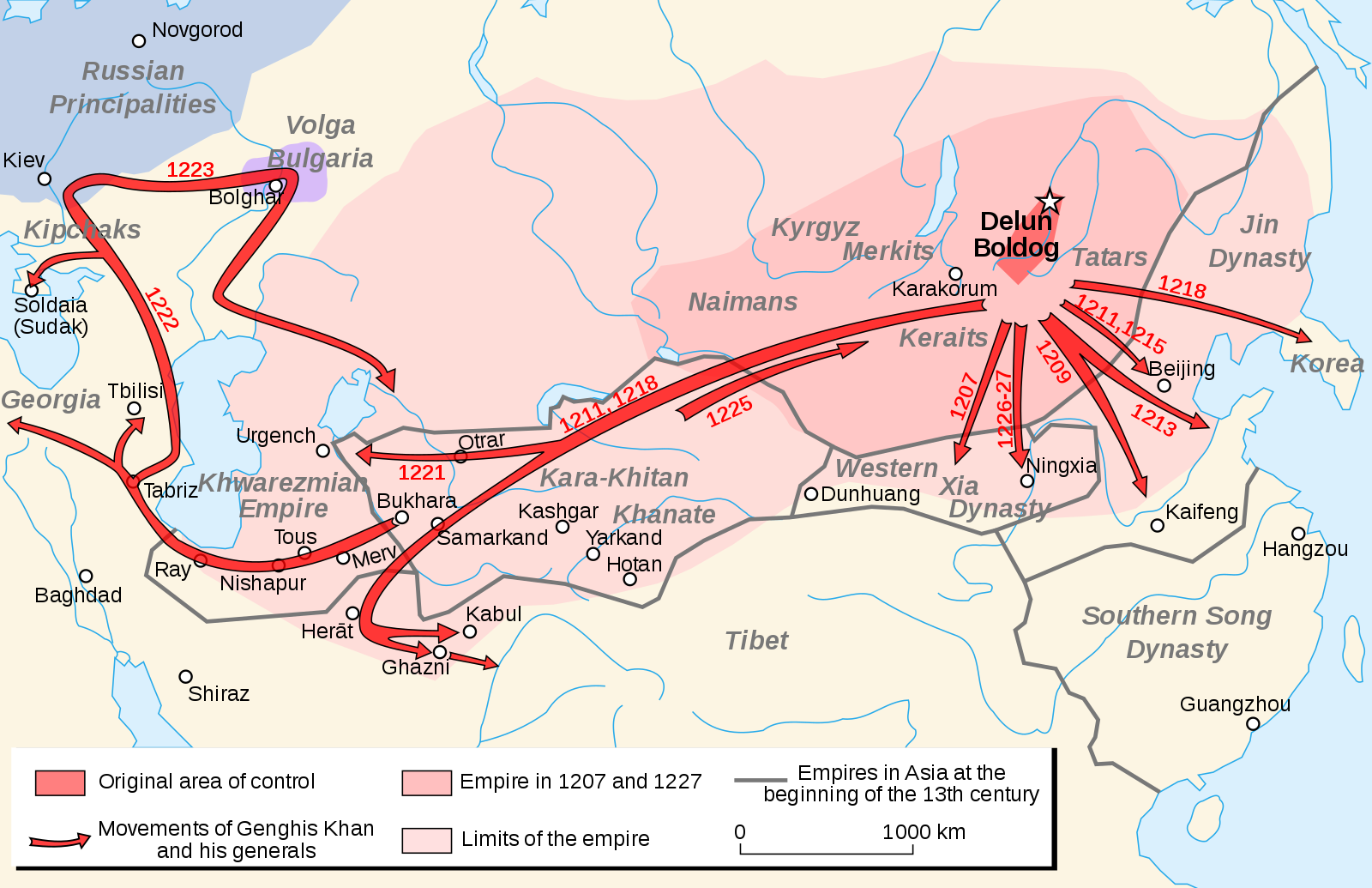
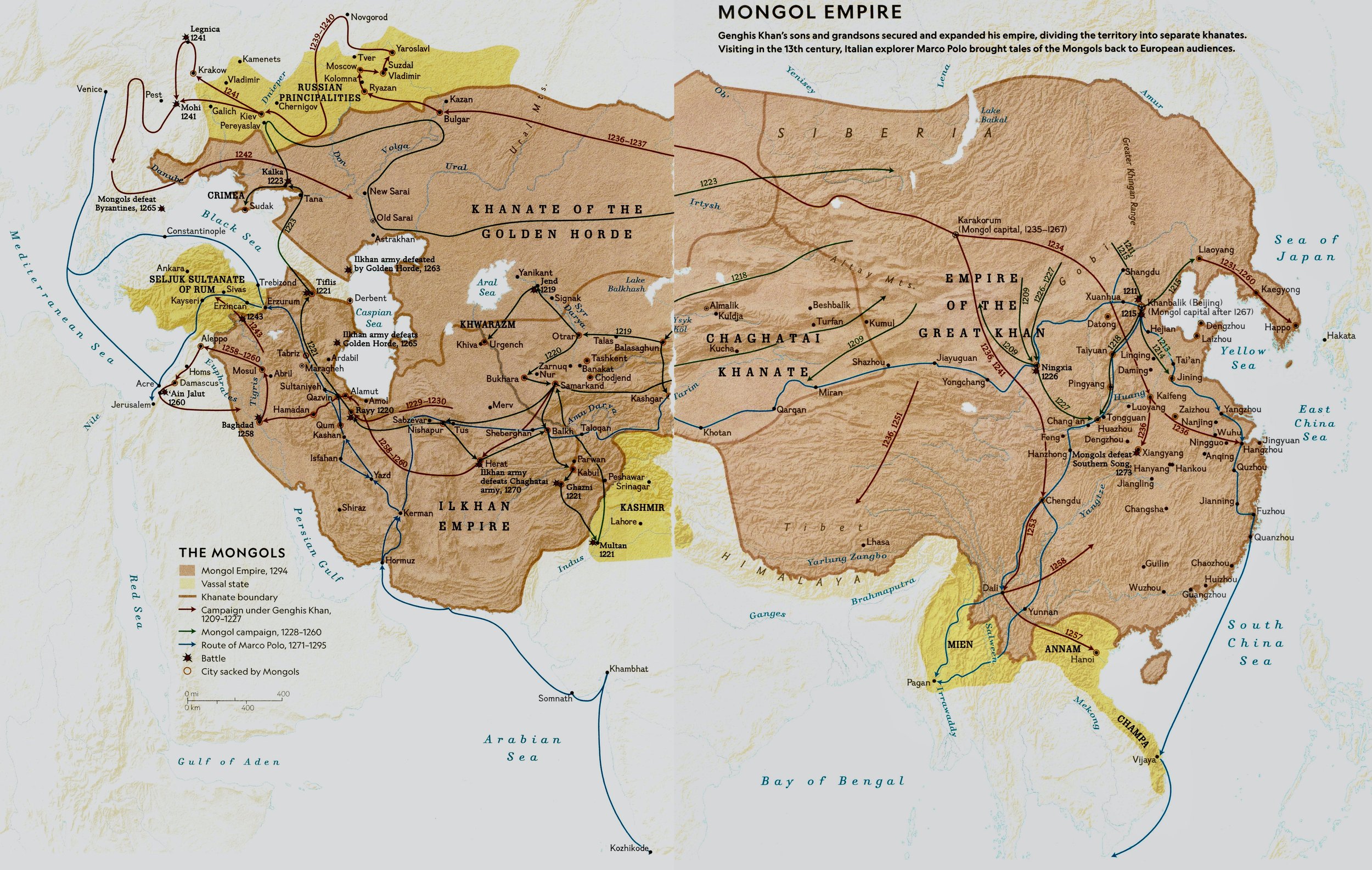
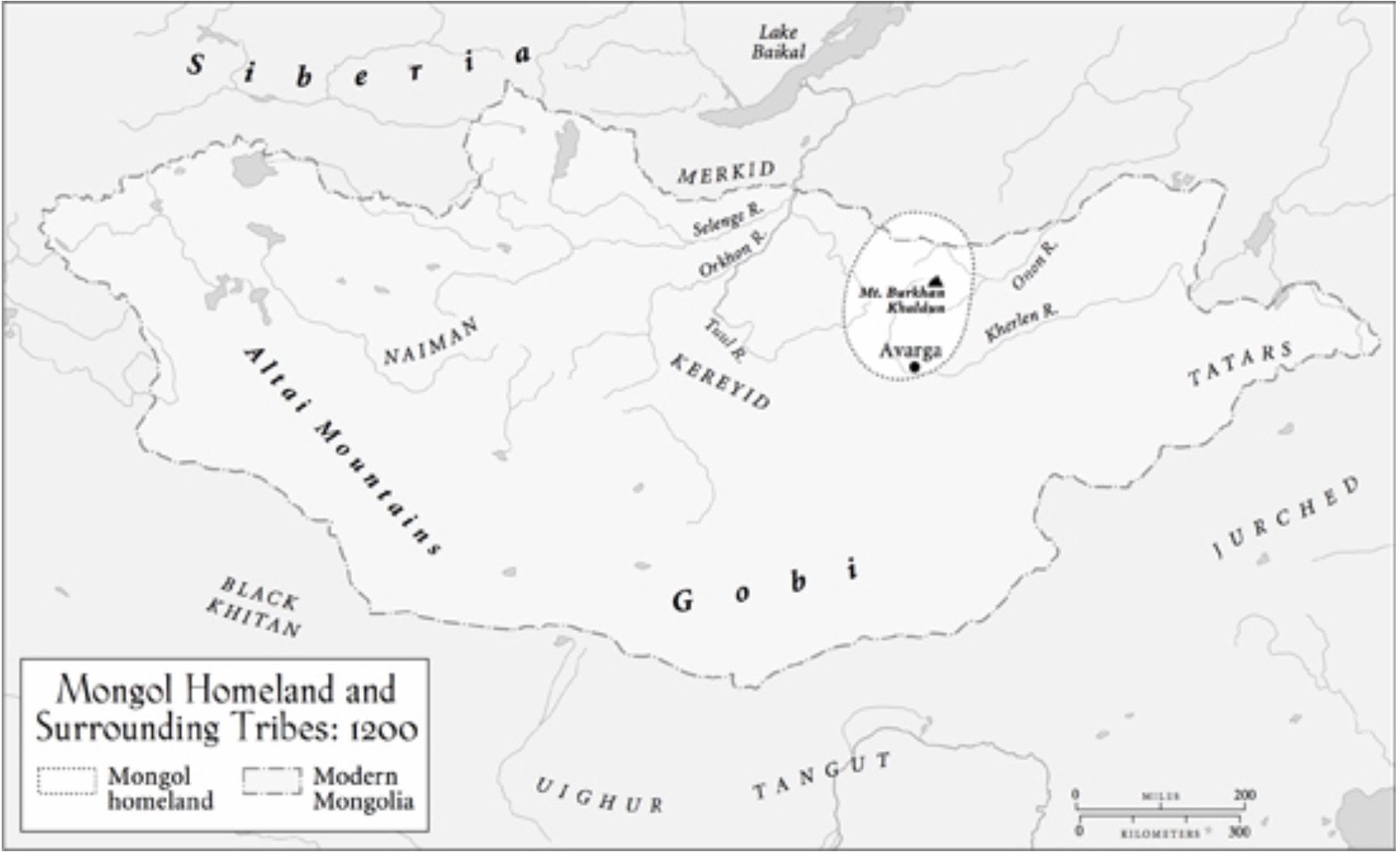
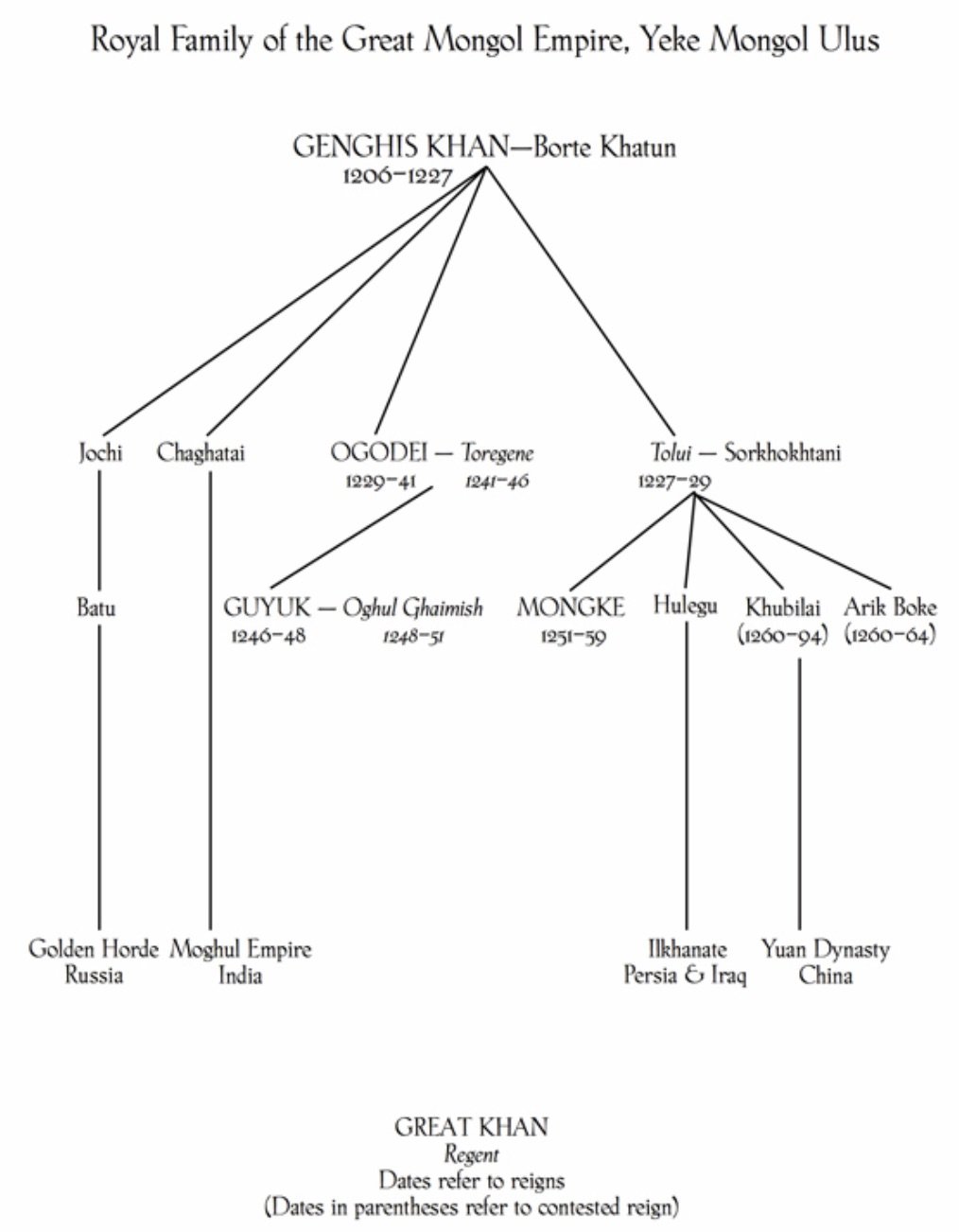
The Mongol Armies
1229: Ögödei, son of Genghis Khan, is elected successor.-War by NatGeo.
1227: Death of Genghis Khan; his burial is conducted in secret.-War by NatGeo.
1219-1223: Fall of the Khwarazm Empire to conquering Mongol Armies.-War by NatGeo.
1219: The Mongols rode into Khawarazm with ~100,000 Mongol warriors and 50,000 allied soldiers and engineers.-War by NatGeo.
1211-1215: Fall of the Chinese Jin Empire to conquering Mongol Armies; the Mongols split their army into three columns that swept around Zhongdu (near modern day Beijing), capturing it in 1215.-War by NatGeo.
1206: Genghis Khan is proclaimed ruler of the unified Mongol clans.-War by NatGeo.
1175: Temujin’s father, Yesugei, is poisoned by Tatar’s, leaving his family impoverished.-War by NatGeo.
1162: Temujin, later Genghis Khan, is born to the Borjigin clan on the Mongolian Steppe.-War by NatGeo.
__________________________________________________________________________________
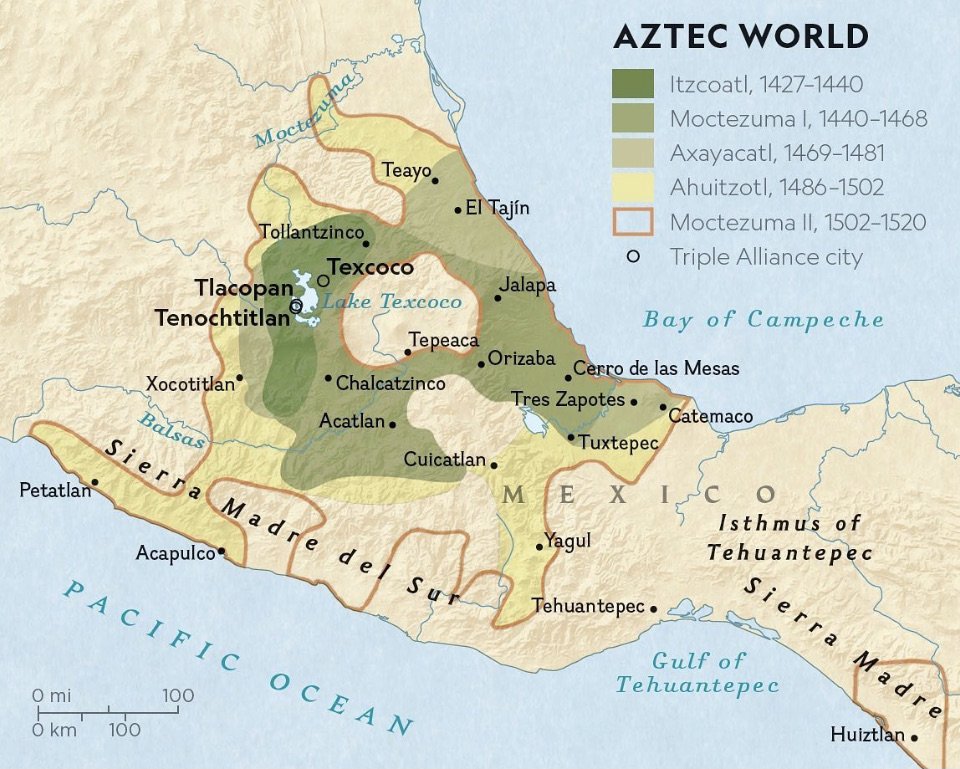
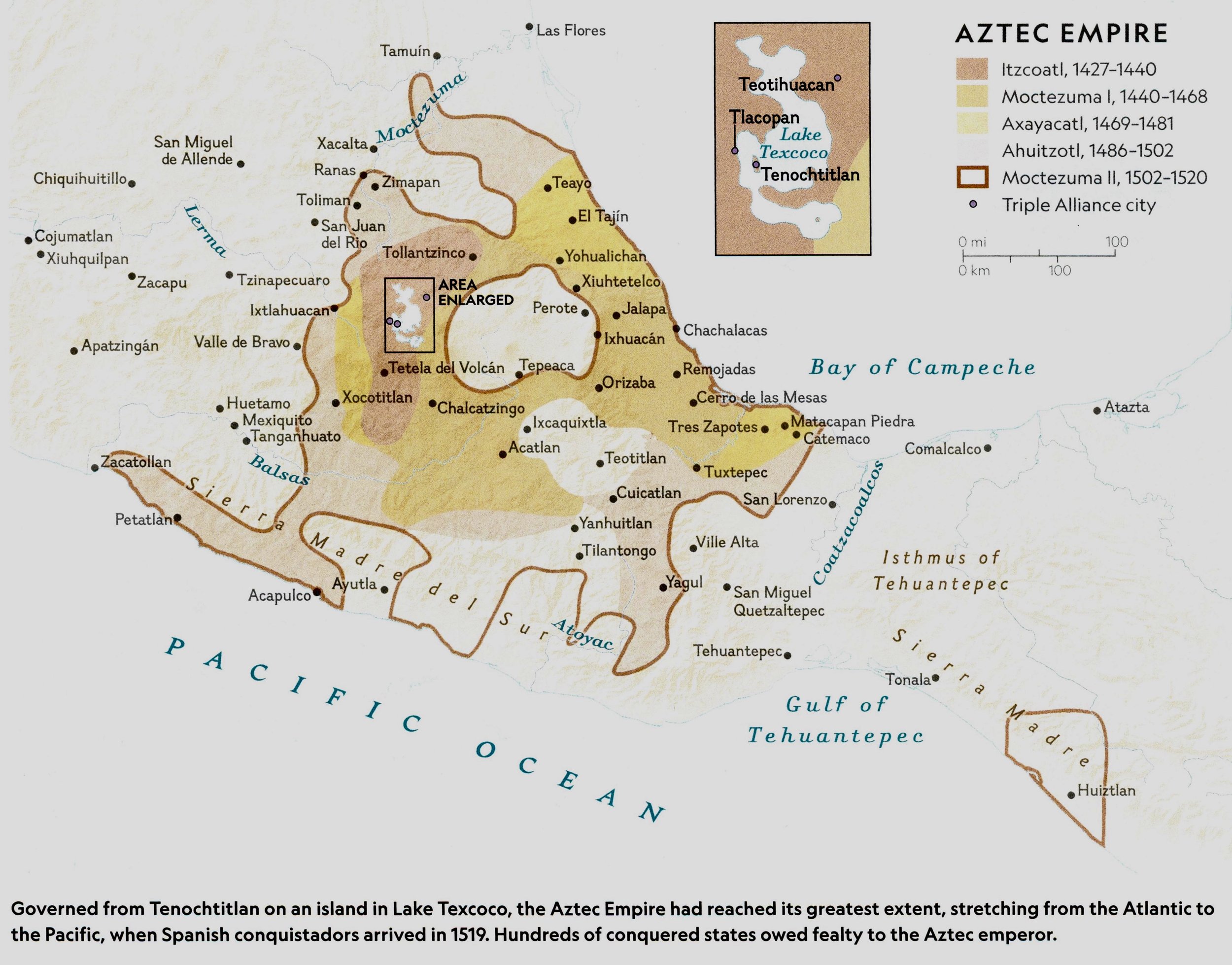
Spanish Colonialism in the America’s
Nov, 1533: Pizarro enters the Inca capital of Cusco without a fight.-War by NatGeo.
Aug, 1533: Pizarro executes Atahualpa by garroting (strangulation).-War by NatGeo.
Nov, 1531: Spanish Pizarro and his soldiers attack the Inca, killing thousands, in the town of Cajamarca and capture Incan King Atahualpa. The Incan bring in literal tons of gold and silver to Pizarro for ransom.-War by NatGeo.
Spring, 1531: Spanish Francisco Pizarro reaches Peru with only 200 men, horses, and guns, and contacts Inca leader Atahualpa.-War by NatGeo.
1528: Francisco Pizarro is made Governor of South American Spanish possessions by Spanish King Charles V.-War by NatGeo.
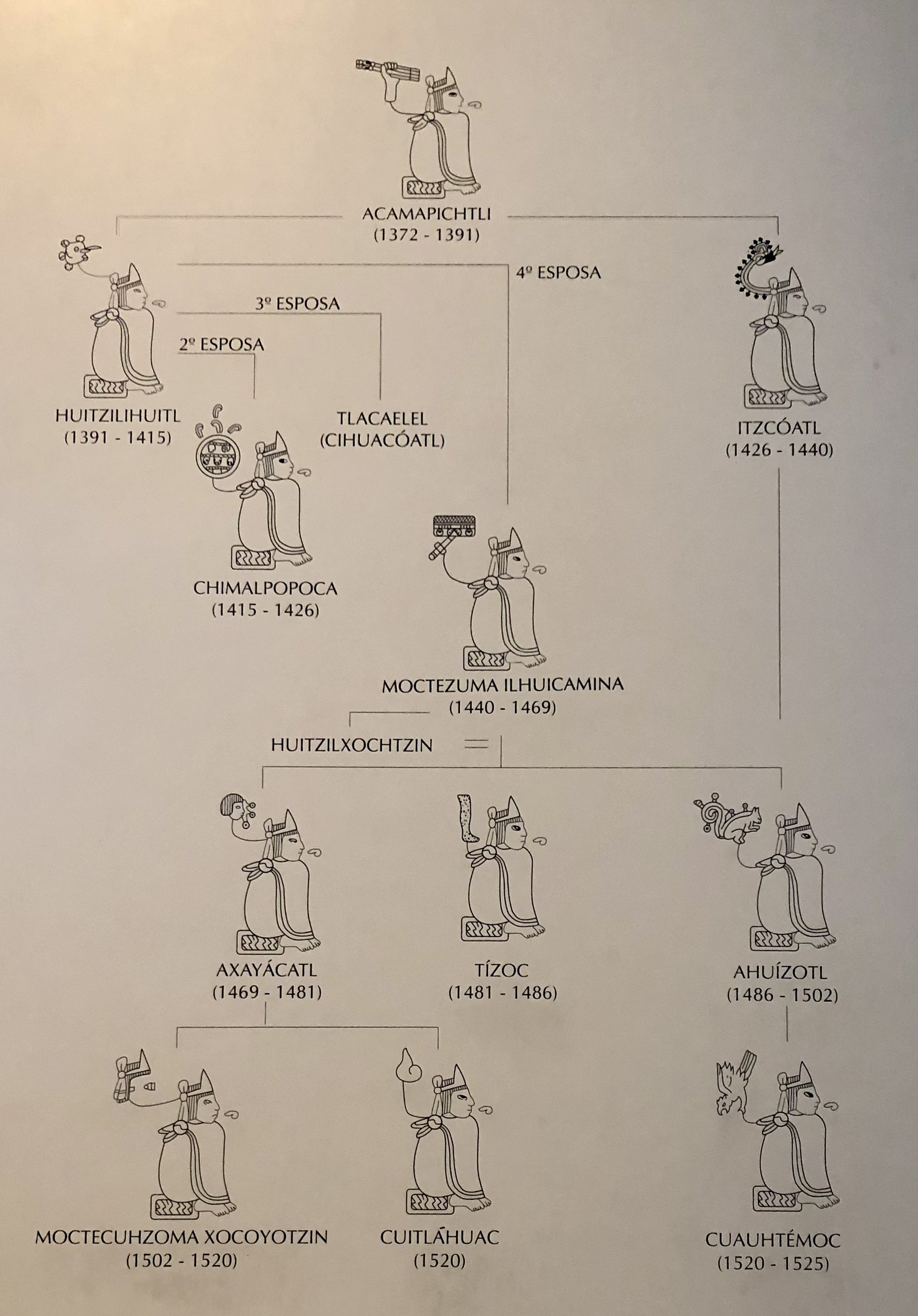
Aug, 1521: Fall of Tenochtitlan; Determined to reconquer the city, Cortés and his armies built a fleet of sailing ships, surrounded and sieged the city. Lacking supplies and under siege, the city surrendered. Approximately 100 Spaniards and 100,000 Aztecan’s had died.-War by NatGeo.
1521: Cortés’ and his armies return to Tenochtitlan; besieged by Revolting Aztec fighters with lances, pelted by stones from citizens on rooftops, most of the Spanish soldiers were killed in what the Spaniard later called the “Night of Sorrows.”-War by NatGeo.
1520: The Aztec retake Tenochtitlan; Cortés’ forces leave Tenochtitlan to deal with a hostile Spanish expedition at the coast and in their absence, lost control of the city.-War by NatGeo.
Nov, 1519: Cortés and his armies march in Tenochtitlan unopposed. Moctezuma II greets Cortés respectfully but was placed under house arrest. Cortés takes control of the city.-War by NatGeo.
1519: Spanish Hernan Cortés sails from Cuba to Mexico with 600 men & 16 horses. They unify with many Aztecan conquered states. Moctezuma II attempted to appease them with gifts of gold before sending wizards to blind them. Cortez’ enters the Aztec capital of Tenochtitlan and takes its leader, Moctezuma II, prisoner.-War by NatGeo.
1502: Moctezuma II succeeds his uncle as leader of the Aztec Empire.-War by NatGeo.
1494: The Treaty of Tordesillas; Pope Alexander VI grants all lands West of a demarcation in the Atlantic to Spain.-War by NatGeo.
__________________________________________________________________________________
Samurai
1876: End of the Samurai era when the Japanese Government forbids the wearing of swords.-War by NatGeo.
1615: Siege of Osaka Castle; Ieyasu besieges Osaka Castle, defeating Hideyori (Hideyoshi’s heir), taking control of Japan.-War by NatGeo.
1603: The Japanese Imperial Court names Ieyasu as Shogun; Ieyasu embarks on construction projects including a vast castle at Edo (later Tokyo).-War by NatGeo.
Oct, 1600: Battle of Sekigahara; Ieyasu’s forces, 89,000 strong, defeat Mitsunari, 82,000 strong, at the village of Sekigahara, NE of Kyoto on a foggy, rainy morning. Two of Mitsunari’s discontented daimyo had secretly told Ieyasu that they would not obey their leader’s orders. When these troops failed to move on his commands, Mitsunari was forced to retreat.-War by NatGeo.
1598: Death of Hideyoshi of Japan. Despite leaving an heir, rival forces face off to seize control. The armies to the west commanded by Ishida Mitsunari, gather together to take on the forces to the East, commanded by Tokugawa Ieyasu.-War by NatGeo.
1590s: Japanese forces under Hideyoshi twice fail to invade Korea.-War by NatGeo.
1590: Unification of Japan under Tomoto Hideyoshi.-War by NatGeo.
1588: The Great Sword Hunt; Hideyoshi confiscates swords from all non-samurai, claiming he needs to melt down the weapons to build a statue of Buddha.-War by NatGeo.
1583: Osaka Castle is built by Toyotomi Hideyoshi.-War by NatGeo.
1582: Death by suicide of Japanese Warlord Nobunaga after he is attacked.-War by NatGeo.
1575: Battle of Nagashino; Nobunaga’s gunmen destroy the enemies advancing calvary from behind a palisade.-War by NatGeo.
1560: The Battle of Okehazama; Japanese warlord Oda Nobunaga rises to prominence after a daring attack on a rival army who had paused in a narrow gorge known as Okehazama. Nobunaga went on to consolidate control of many of his opponent’s territories.-War by NatGeo.
1550s: Three Daimyo rule Japan- Oda Nobunaga, Toyotomi Hideyoshi, and Tokugawa Ieyasu.-War by NatGeo.
1549: Jesuit Missionaries reach Japan and begin converting the Japanese to Christianity.-War by NatGeo.
1543: Introduction of the Harquebus (firearm) to Japan by Shipwrecked Portuguese Sailors.-War by NatGeo.
__________________________________________________________________________________
American Revolution
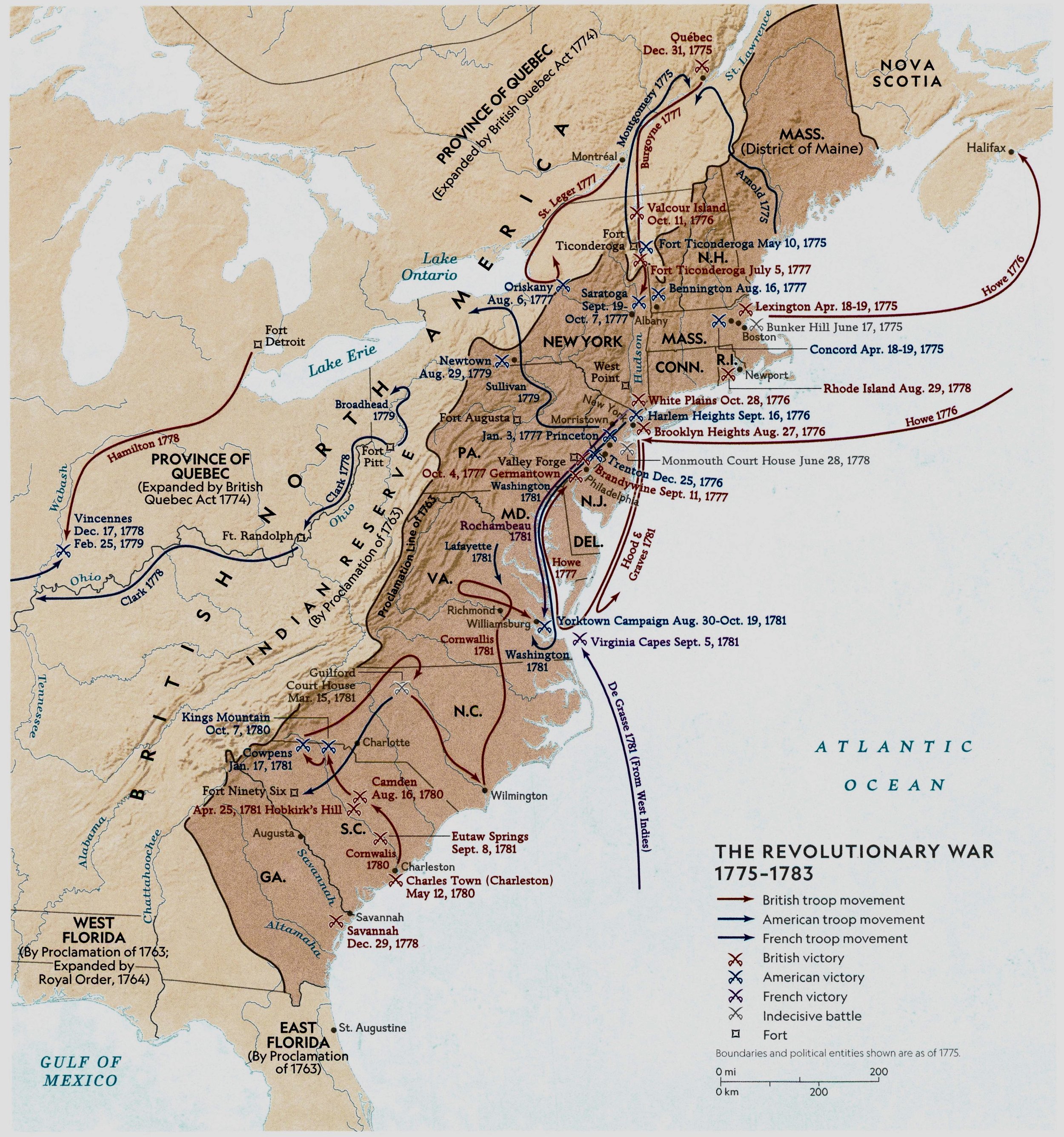
3 Sep, 1783: The Treaty of Paris is signed by the USA and Great Britain, formally ending the war.-War by NatGeo.
19 Apr, 1775- 19 Oct, 1781: The American Revolutionary War; American Colonies allied with France defeat British Forces. ~13,000 Americans were killed or wounded with some 20,000 taken prisoner with ~24,000 British casualties including prisoners.-War by NatGeo.
19 Oct, 1781: Battle of Yorktown; British forces under Cornwallis surrender with 7,000 men to Colonial forces under Washington at Yorktown, VA.-War by NatGeo.
8 Sep, 1781: The Battle of Eutaw Springs; British Victory.-War by NatGeo.
5 Sep, 1781: The Battle of Virginia Capes; French Victory.-War by NatGeo.
25 Apr, 1781: The Battle of Hobkirk’s Hill; British Victory.-War by NatGeo.
15 Mar, 1781: The Battle of Guilford Court House; indecisive.-War by NatGeo.
17 Jan, 1781: The Battle of Cowpens; American Victory.-War by NatGeo.
7 Oct, 1780: The Battle of Kings Mountain; American Victory.-War by NatGeo.
16 Aug, 1780: The Battle of Camden; British Victory.-War by NatGeo.
12 May, 1780: The Battle of Charles Town; British victory.-War by NatGeo.
29 Dec, 1778: The Battle of Savannah; British victory.-War by NatGeo.
29 Aug, 1778: The Battle of Rhode Island; British victory.-War by NatGeo.
1778: The French enter the American Revolutionary War on the American Side.-War by NatGeo.
19 Sep-17 Oct, 1777: The Battle of Saratoga in upstate NY, a turning point in the war which persuades the French to enter on the American side; Continental Commander Horatio Gates with 8-10K troops holds off British troops under Burgoyne, who surrenders with some 6K troops.-War by NatGeo.
4 Oct, 1777: The Battle of Germantown; British Victory.-War by NatGeo.
11 Sep, 1777: The Battle of Brandywine; British Victory.-War by NatGeo.
16 Aug, 1777: The Battle of Bennington; American Victory.-War by NatGeo.
5 Jul, 1777: The Battle of Ticonderoga; British Victory.-War by NatGeo.
3 Jan, 1777: The Battle of Princeton; American Victory.-War by NatGeo.
25 Dec, 1776: The Battle of Trenton; American Victory.-War by NatGeo.
28 Oct, 1776: The Battle of White Plains; British Victory.-War by NatGeo.
11 Oct, 1776: The Battle of Valcour Island; British Victory.-War by NatGeo.
16 Sep, 1776: The Battle of Harlem Heights; American Victory.-War by NatGeo.
27 Aug, 1776: The Battle of Brooklyn Heights; British Victory.-War by NatGeo.
4 Jul, 1776: The Declaration of Independence is adopted by the Second Continental Congress.-War by NatGeo.
31 Dec, 1775: The Battle of Quebec; British Victory.-War by NatGeo.
17 Jun, 1775: The Battle of Bunker Hill; indecisive.-War by NatGeo.
10 May, 1775: The Battle of Fort Ticonderoga; Colonial forces defeat British Forces.-War by NatGeo.
19 Apr, 1775: The Battles of Lexington and Concord ignite the American Revolutionary War; British MGEN Thomas Gage learns that the colonists had stockpiled guns and powder in Concord and deploys ~1K troops from Boston to confiscate the weapons. Dispatch riders including Paul Revere had ridden out the night before to warn the approaching soldiers. Mass Minutemen were waiting as the Redcoats marched into the town of Lexington. Someone fired, possibly accidentally, and the British fired upon the minutemen, killing or wounding 8 colonial defenders. The colonists fled and the British marched on to Concord to find the supplies gone and about 400 militiamen waiting for them. After a firefight, the British retreated and turned back toward Boston. Colonists harassed them along the way. By the time the redcoats reached safety, they had lost more men than the colonists.-War by NatGeo.
5 Mar, 1770: The Boston Massacre; 11 colonists are shot with 5 killed in front of the Custom House in Boston by British soldiers.-War by NatGeo.
1765: The Stamp Act and the Quartering Act are enacted on the Colonies by Britain.-War by NatGeo.
1763: The French & Indian War; Britain wins France’ Canadian territories but doubles their national debt. British Parliament thought it only reasonable to levy taxes on its American colonies to cover these expenses.-War by NatGeo.
__________________________________________________________________________________
Napoleonic Wars
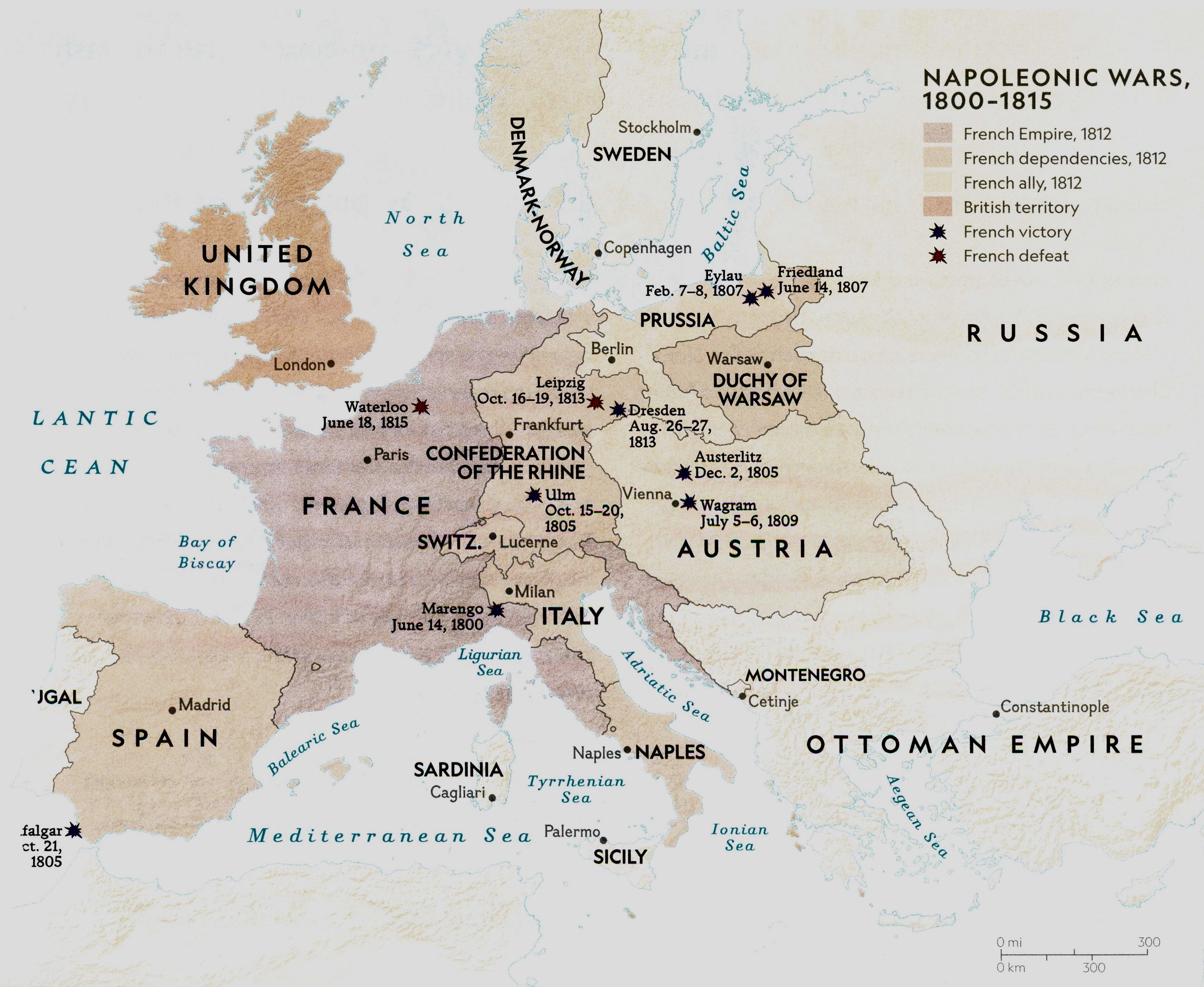
18 Jun, 1815: The Battle of Waterloo; the French are defeated by an English- Prussian force led by Arthur Wellesley, duke of Wellington, at Waterloo in Belgium.-War by NatGeo.
1815: Napoleon escapes Elba and reunites the French Armies.-War by NatGeo.
1814: Abdication of Napoleon; he is exiled to Elba.-War by NatGeo.
26-27 Aug, 1813: The Battle of Dresden; French forces defeat allied forces.-War by NatGeo.
16-19 Aug, 1813: The Battle of Leipzig; Allied forces defeat French forces.-War by NatGeo.
1812: France invades Russia; Napoleon launches a massive attack on Russia with upwards of half a million men. They are forced to retreat with heavy casualties.-War by NatGeo.
7 Sep, 1812: The Battle of Borodino; French forces under Napoleon defeat Imperial Russian forces under General Mikhail Kutuzov-War by NatGeo.
5-6 Jul, 1809: The Battle of Wagram; French forces defeat Allied forces.-War by NatGeo.
14 Jun, 1807: The Battle of Friedland; French forces defeat Allied forces.-War by NatGeo.
7-8 Feb, 1807: The Battle of Eylau; French forces defeat Allied forces.-War by NatGeo.
2 Dec, 1805: Battle of Austerlitz; French forces, 68,000 strong, defeat a combined Austrian- Russian force of 90,000. The battle forces the Austrians to make peace with the French and the Russian troops to return home.-War by NatGeo.
21 Oct, 1805: Battle of Trafalgar; the British Royal Navy under Admiral Horatio Nelson defeat the French Navy under Admiral Pierre de Villeneuve; the French with 33 ships attempt to slip out of the Spanish port of Cadiz to sail to Naples, Italy, to support Napoleon’s campaigns. Nelson’s 27 ships caught up with the French off Cape Trafalgar. Separating into two squadrons, the British attack from front and rear and managed to split the French fleet. After five hours of fierce fighting, the British capture 17 ships and 20K men losing 449 sailors to the French’s 4408. Nelson himself was shot and died.-War by NatGeo.
15-20 Oct, 1805: The Battle of Ulm; French forces defeat Allies.-War by NatGeo.
1804: Napoleon crowns himself Emperor of France.-War by NatGeo.
1803: Britain declares war on France.-War by NatGeo.
1802: Treaty of Amiens brings temporary peace between France and Britain.-War by NatGeo.
14 Jun, 1800: The Battle of Marengo; French forces defeat Allied forces.-War by NatGeo.
1799: French Military Coup; Napoleon Bonaparte becomes French First Consul.-War by NatGeo.
__________________________________________________________________________________
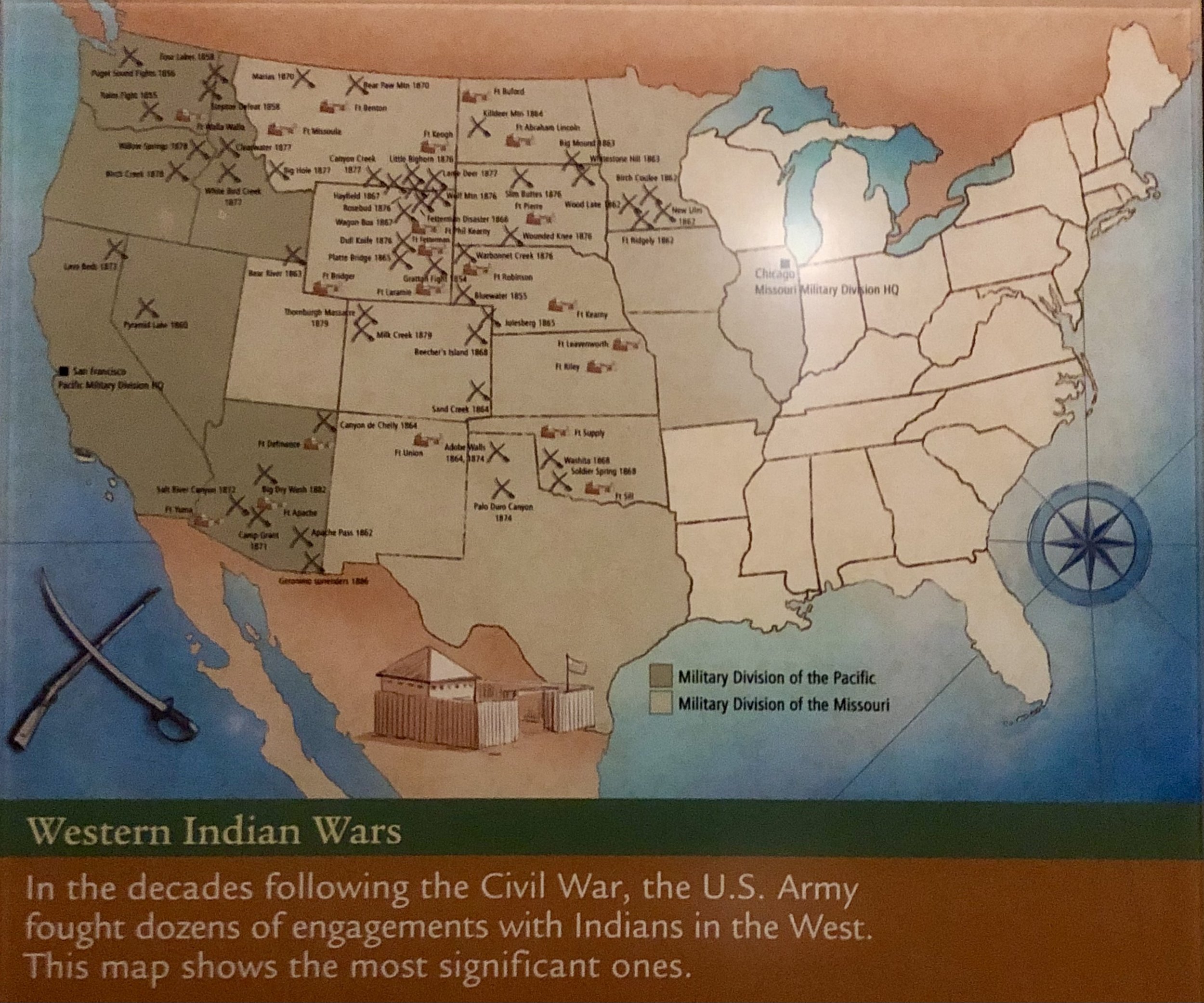
The Plains Wars
1890: Battle of Wounded Knee; US Army troops kill several hundred Lakota Sioux near Wounded Knee, SD while the Lakota are disarming.-War by NatGeo.
1880s: Most of the Plains Indians are confined to reservations.-War by NatGeo.
25 Jun, 1876: The Battle of Little Bighorn; Sioux, Cheyenne, and Arapaho fighters defeat US Soldiers. Custer divides his forces into several companies. Two attack the Southern end of the village but are driven back by their mounted opponents. Custer’s 210 men are completely wiped out.-War by NatGeo.
Mar, 1876: Three forces of cavalry and infantry advance out of forts in MT, the Dakota, and WY territories, among them is LtCol George Armstrong Custer, commanding the 7th Cav.-War by NatGeo.
1875: The Commissioner of Indian Affairs orders all Sioux to confine themselves to the Dakota Reservation by the end of Jan, 1876. Many of the Indians refuse to move.-War by NatGeo.
1874: A Gold Rush brings US Settlers to the Black Hills in violation of the Second Treaty of Fort Laramie.-War by NatGeo.
1868: The Second Treaty of Fort Laramie is signed by some Sioux leaders, requiring the Sioux to settle on a reservation in the Dakota Territory, granting them rights to the Black Hills.-War by NatGeo.
1866: 80 US Soldiers are killed by Sioux, Cheyenne, and Arapaho on the Bozeman Trail near Fort Phil Kearny, WY.-War by NatGeo.
Nov, 1864: The Cheyenne Village Massacre is perpetrated by Col. John Chivington at Sand Creek, CO (“We Must Kill Them Big or Little”).-War by NatGeo.
Jul, 1864: Second Sioux War; US Forces fight the Sioux in the Dakota territory.-War by NatGeo.
Battle of Killdeer Mountain; BGEN Alfred Sully defeats Sitting Bull and Inkpaduta.-War by NatGeo.
1854-1855: First Sioux War; Lakota Sioux combat US Armed Forces in the Dakota Territory.-War by NatGeo.
__________________________________________________________________________________
US Civil War
12 Apr, 1861- 1865: The US Civil War; ~620,000, 2% of the US population, die.-War by NatGeo.
9 Apr, 1865: End of the US Civil War; Confederate Forces under Lee surrender to Union Forces under Grant at Appomattox Court House, VA. As part of the terms, all Confederate soldiers’ are granted parole if they pledge no longer to take up arms against the US.-War by NatGeo.
1864: Sherman’s March to the Sea; Union forces destroy bridges, tear up railroad lines, and pillage farms.-War by NatGeo.
1864: Ulysses S. Grant is named General in Chief of the Union Armies.-War by NatGeo.
1-3 Jul, 1863: The Battle of Gettysburg; Union General George Meade defeats Confederate General Robert E. Lee, ending his second invasion of the North. The total killed and wounded numbered 51K.-War by NatGeo.
18 May- 4 Jul, 1863: The Siege of Vicksburg by US General Ulysses S. Grant; with their surrender, Union forces take control of the river and split the confederacy in two.-War by NatGeo.
4 Jul, 1863: Vicksburg and neighboring Port Hudson surrender to US Forces.-War by NatGeo.
30 Apr- 6 May, 1863: The Battle of Chancellorsville (‘Lee’s Perfect Battle’). Although outnumbered, Lee divides his force and defeats Union forces. Gen. Thomas “Stonewall” Jackson is struck by friendly fire, requiring the amputation of his left arm. He dies of pneumonia 8 days later.-War by NatGeo.
1 Jan, 1863: The Emancipation Proclamation goes into effect, freeing slaves in Confederate States (it did not apply to states outside the confederacy).-War by NatGeo.
17 Sep, 1862: The Battle of Antietam near Antietam Creek in Sharpsburg, Maryland ends Confederate General Robert E. Lee’s first invasion of the North. Lee loses some 6K killed and 17K wounded. Lincoln issues the Emancipation Proclamation after vowing that he would declare freedom for slaves if Lee was driven back.-War by NatGeo.
21 Jul, 1861: First Battle of Bull Run; Confederate forces under Bureaugard and Jackson drive back Union forces under BGEN McDowell on the banks of Bull Run Creek near Manassas, VA. Confederate casualties run to 1750 men; the US lost ~2950.-War by NatGeo.
13-15 Apr, 1861: Lincoln calls on 75,000 militiamen to enlist for the union.-War by NatGeo.
12 Apr, 1861: Confederate forces fire on Fort Sumpter, SC, igniting the US Civil War. The fort falls the following day to Confederate Forces.-War by NatGeo.
8-9 Feb, 1861: Formation of the Confederate States of America (CSA).-War by NatGeo.
6 Nov, 1860: Abraham Lincoln is elected POTUS.-War by NatGeo.
1858: Abraham Lincoln declares “this government cannot endure permanently half slave and half free.”-War by NatGeo.
__________________________________________________________________________________
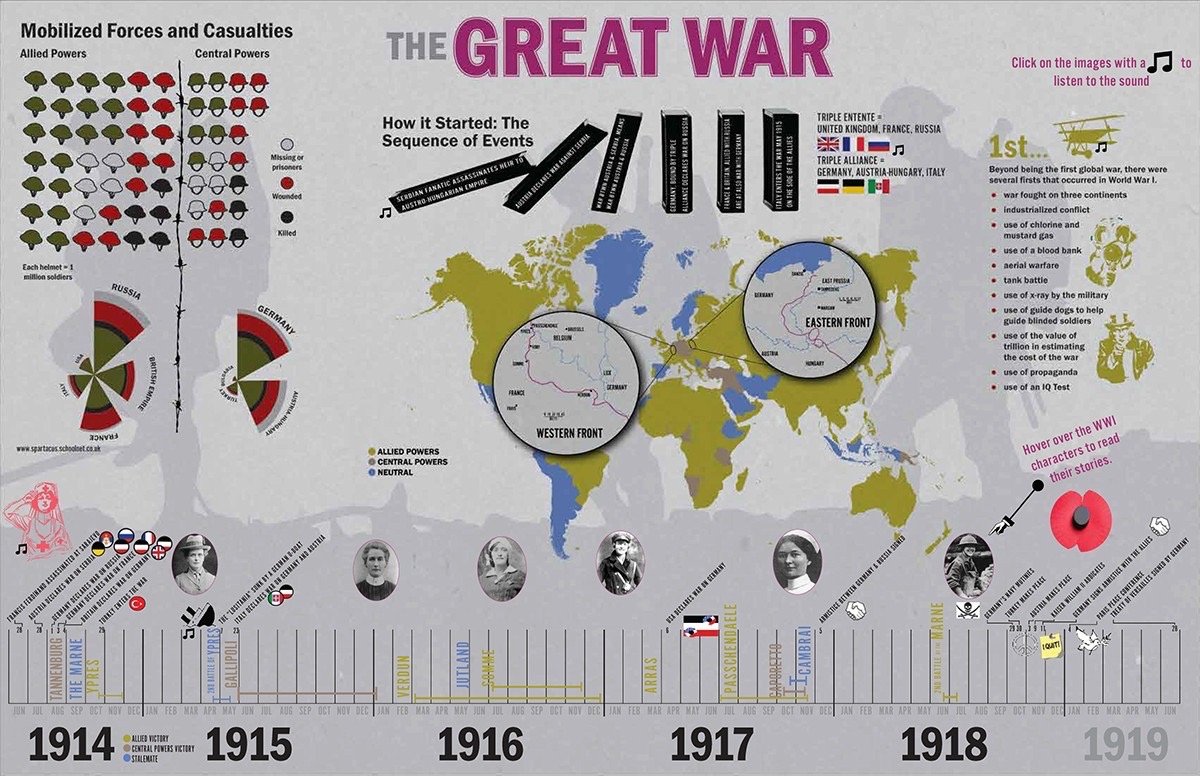
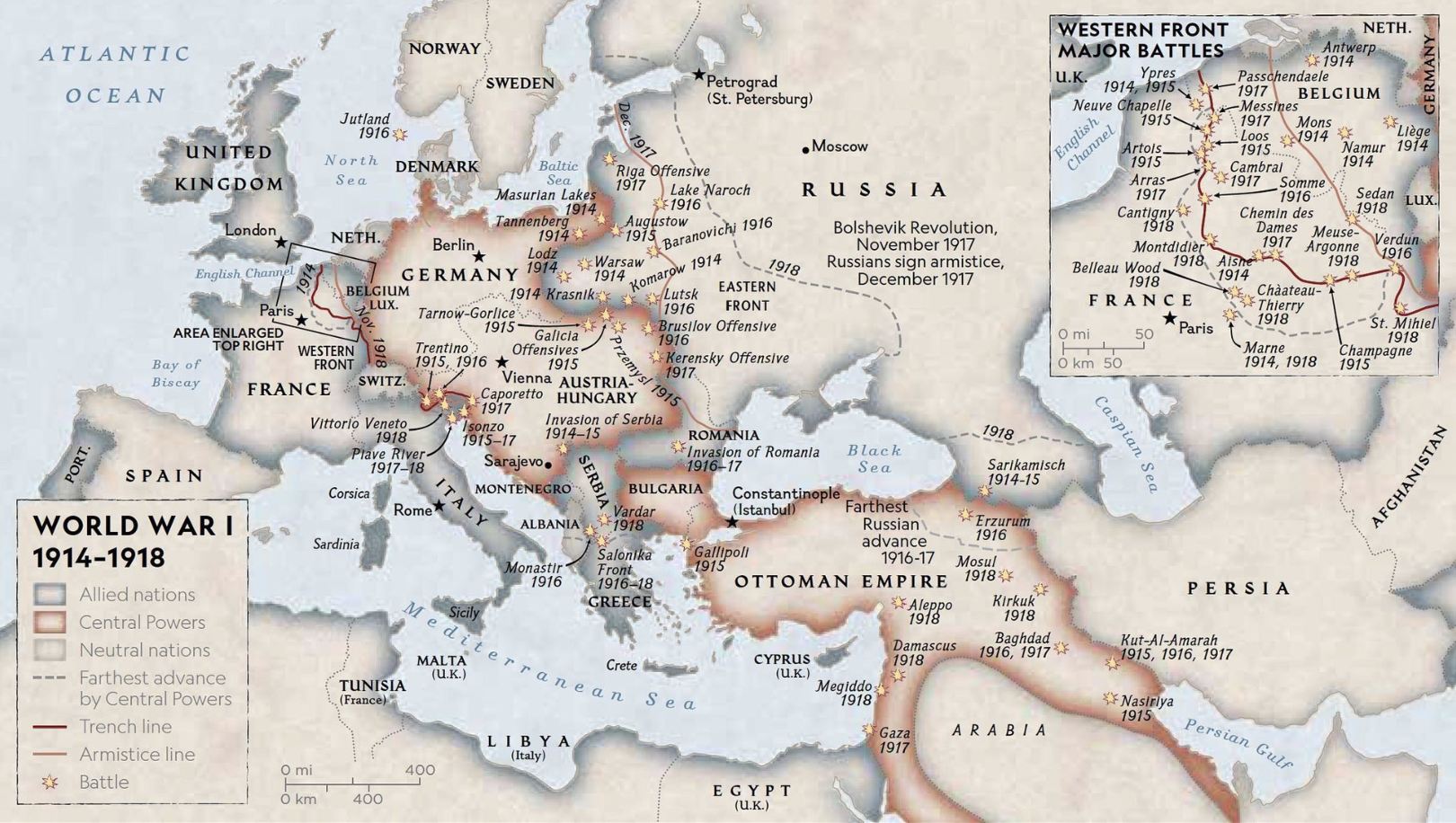
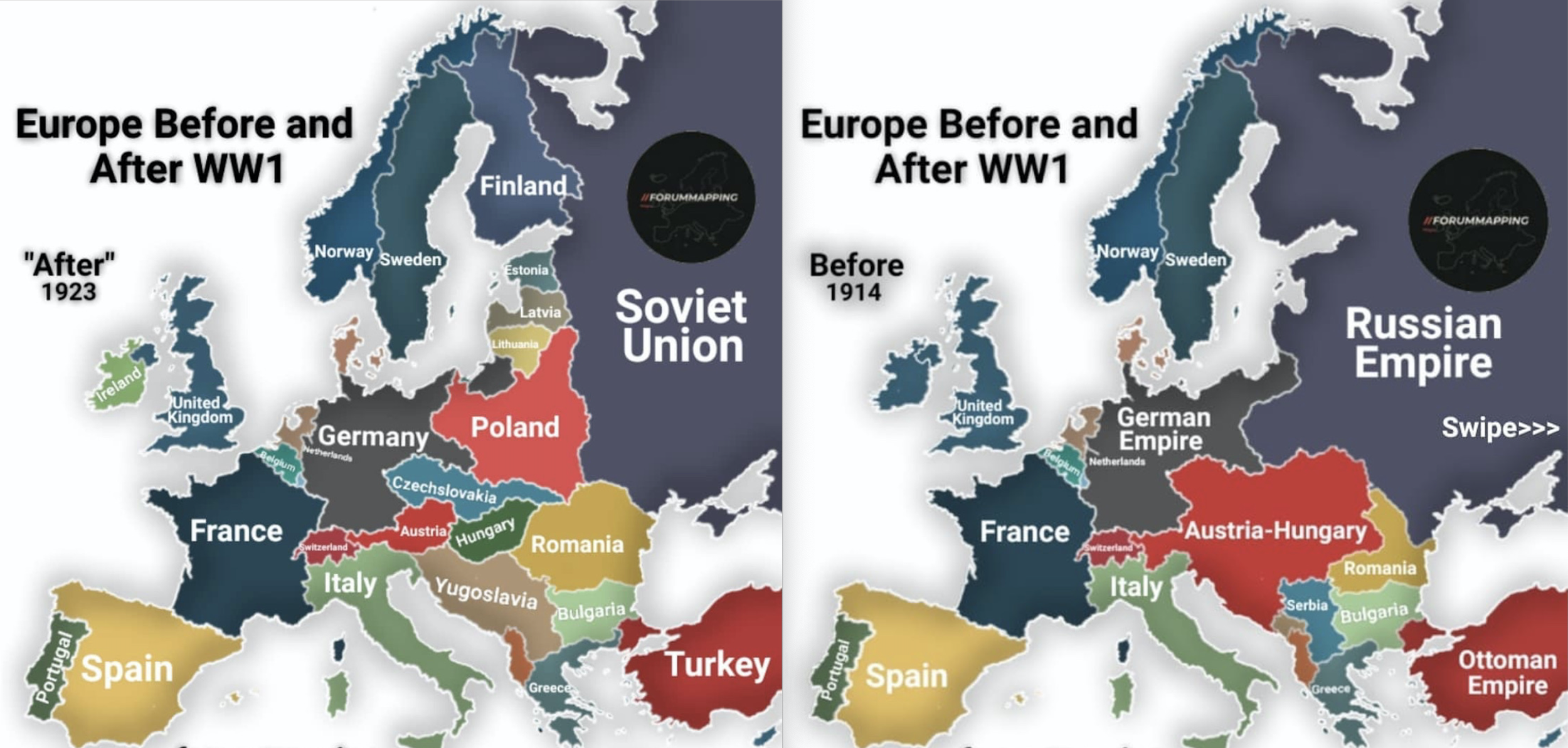
The War to End All Wars
11 Nov, 1918: End of WWI; An Armistice is signed at Compiegne, France. In all, ~9M soldiers and 6M civilians are killed. Chemical Weapons including Choking and Blister Agents kill ~90K.-War by NatGeo.
8 Aug, 1918: The Hundred Days Offensive is launched by American forces on the Western Front; each side suffers >1M casualties.-War by NatGeo.
26K Americans are killed in the Meuse-Argonne portion of the campaign.-War by NatGeo.
6 Apr, 1917: The USA declares war on Germany.-War by NatGeo.
Jul- Nov, 1916: Battle of the Somme; >1M men are killed or wounded.-War by NatGeo.
Feb- Dec, 1916: Battle of Verdun; ~1M men are killed or wounded.-War by NatGeo.
Apr, 1915: The Battle of Ypres marks the first large-scale use of chemical weapons in war. “There staggered into our midst French soldiers, blinded, coughing, chests heaving, faces an ugly purple color, lips speechless with agony, and behind them in the gas-soaked trenches, we learned that they had left hundreds of dead and dying comrades.”-War by NatGeo.
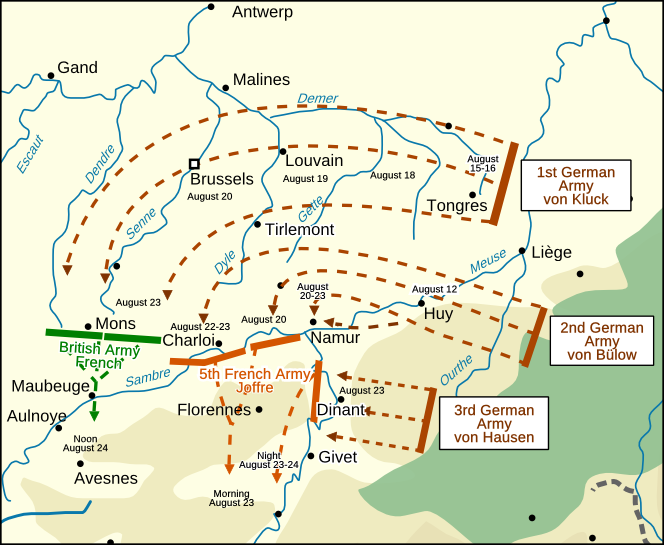
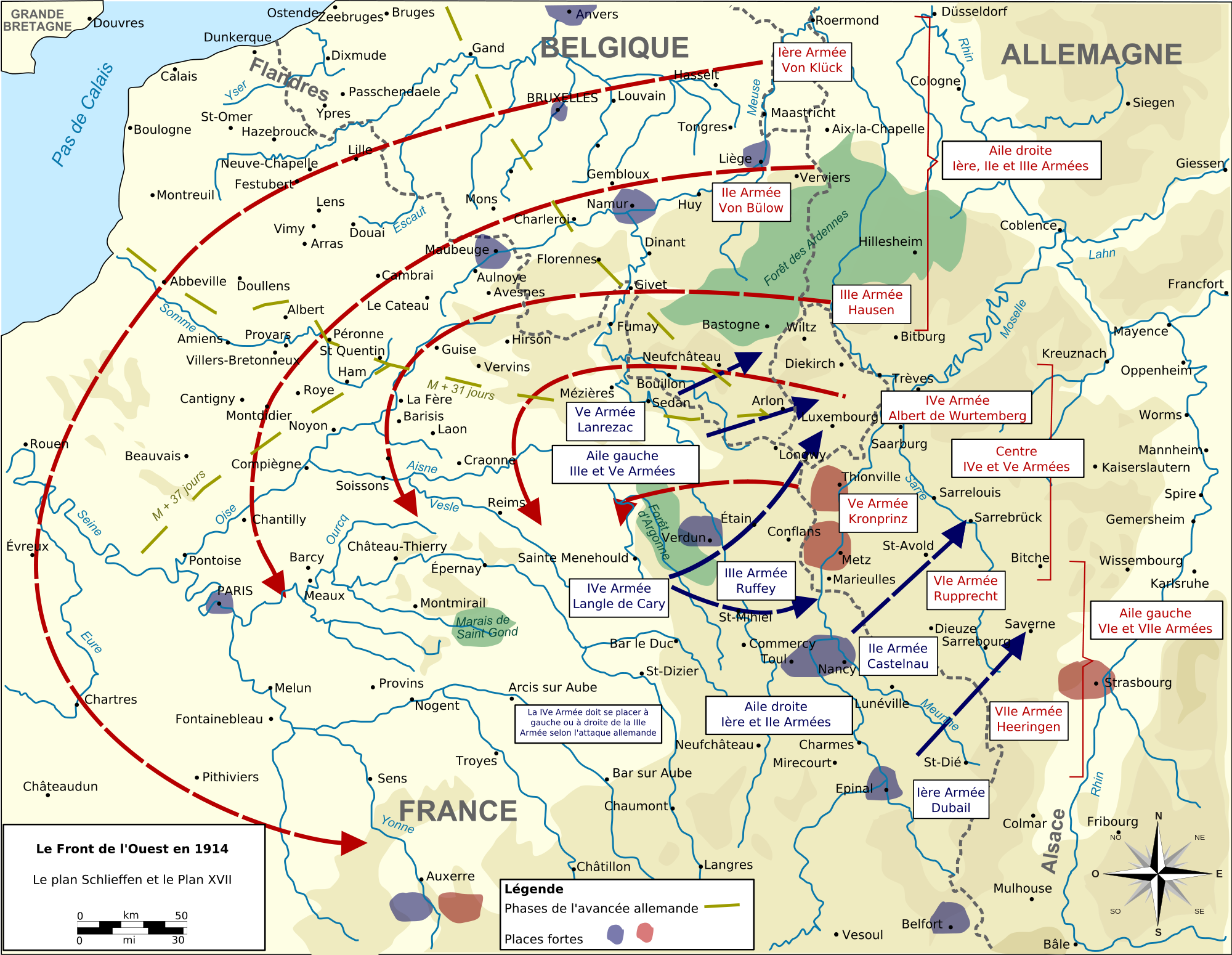
8 Sep, 1914: First Battle of the Marne; Allied forces halt the German advance into France.-War by NatGeo.
2-7 Aug, 1914: Germany invades Belgium enroute to France.-War by NatGeo.
28 Jul, 1914: Austria-Hungary declares war on Serbia.-War by NatGeo.
28 Jun, 1914: Assassination of Austrian Archduke Ferdinand by Serbian Nationalists.-War by NatGeo.
__________________________________________________________________________________
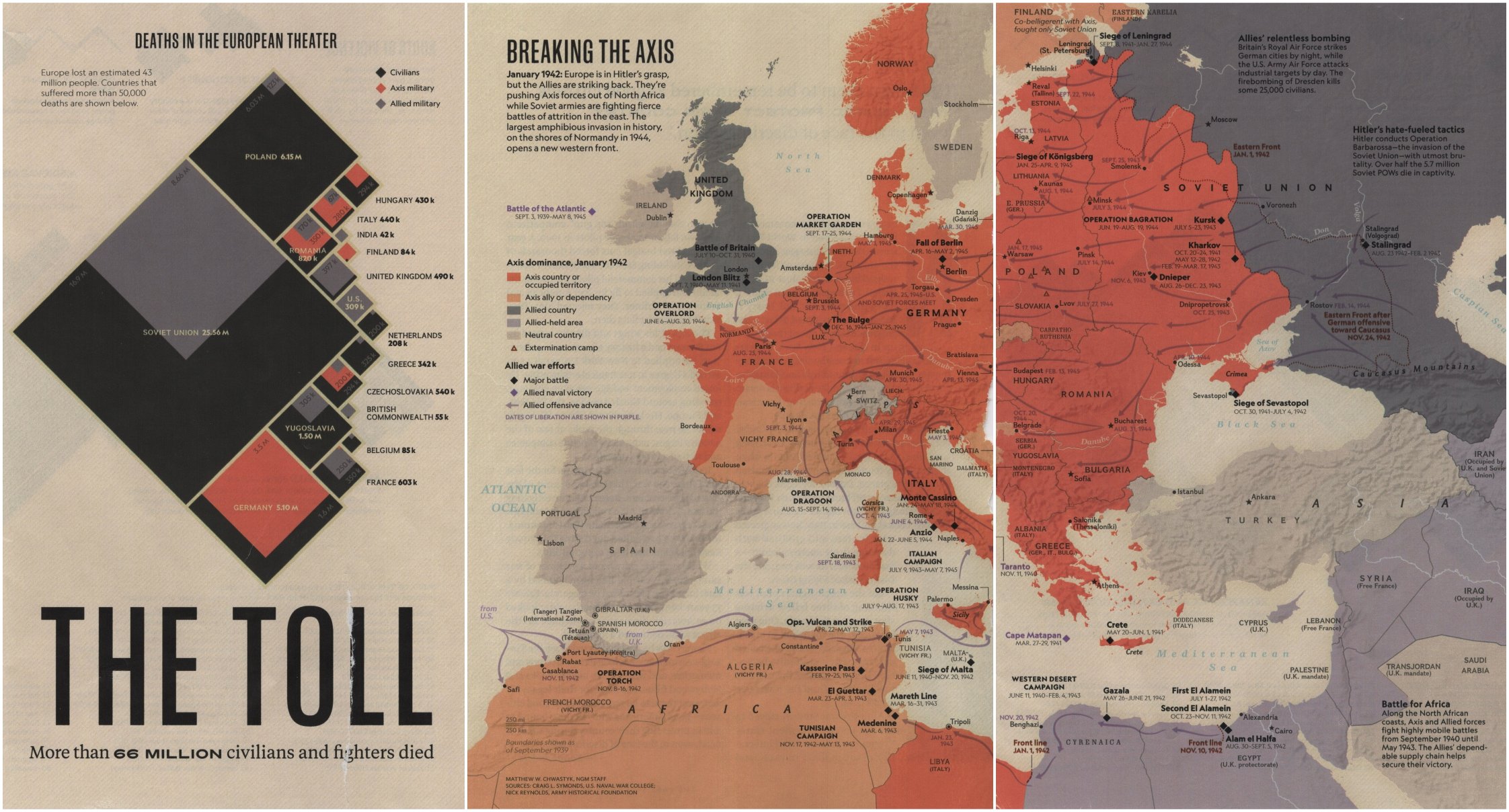
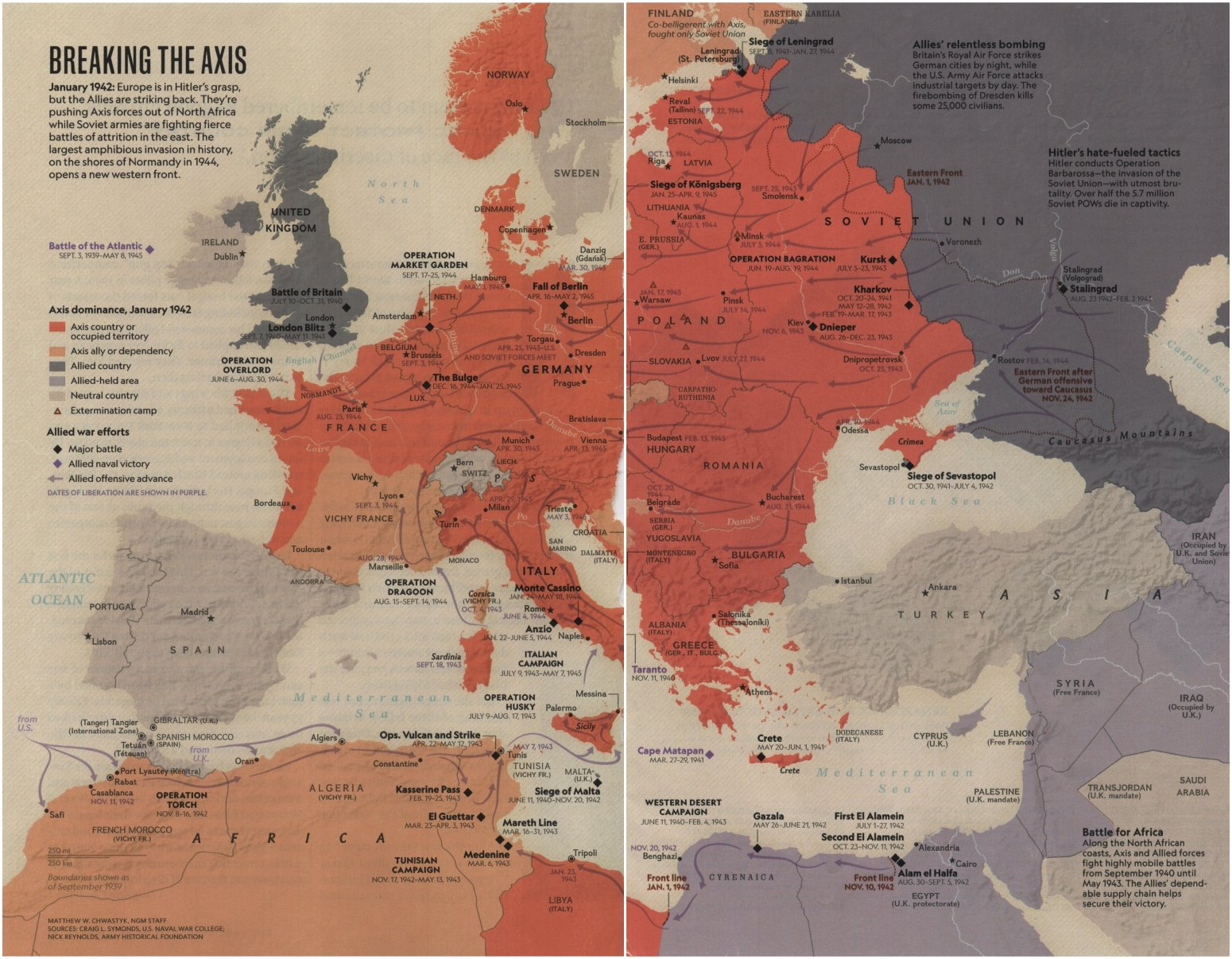
WWII: The World Divided- Europe
7 May, 1945: V-E Day; Germany under Admiral Karl Doenitz surrenders to Allied Forces.-War by NatGeo.
Mar, 1945: US Forces crosses the Rhine River enroute Berlin.-War by NatGeo.
Dec, 1944: Battle of the Bulge; A German counterattack fails to stop the Allied advance.-War by NatGeo.
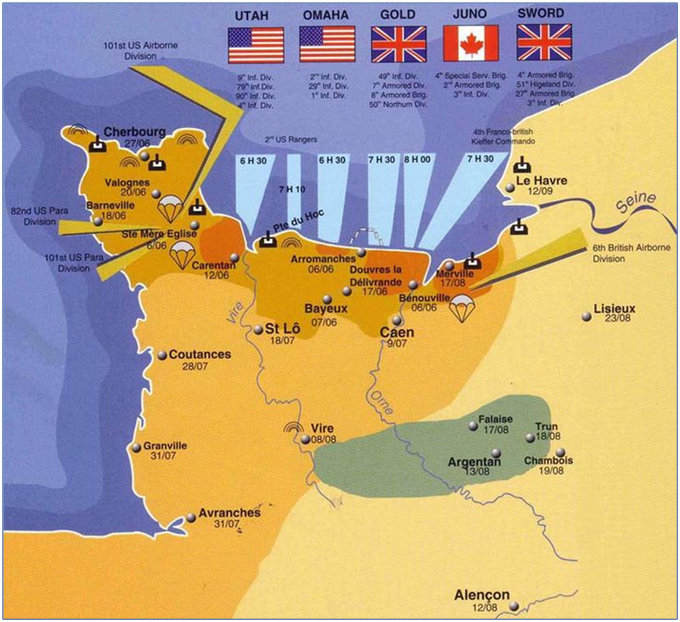
6 Jun, 1944: D-Day (Operation Overlord); Under heavy fire, more than 150,000 Allied troops wade ashore and invade Normandy, France, gaining a footing in continental Europe. Once on land, the allies managed to liberate Holland, Belgium, and France, with Paris retaken on 25 Aug.-War by NatGeo.
Sep, 1943: The Allies invade Italy.-War by NatGeo.
Jan- 2 Feb, 1943: The Battle of Stalingrad results in ~800K Axis casualties and >1M Soviet casualties.-War by NatGeo.
2 Feb, 1943: Surrender of German at Stalingrad after being trapped and starved in the city by Soviet forces.-War by NatGeo.
Jun, 1941: Hitler breaks his non-aggression treaty with the USSR and invades Russia.-War by NatGeo.
1941-1945: The Holocaust is carried out by German SS, primarily in concentration camps in occupied Poland; ~6M Jews and hundreds of thousands of others, including Romany, homosexuals, Jehovah’s Witnesses, and people with disabilities are murdered.-War by NatGeo.
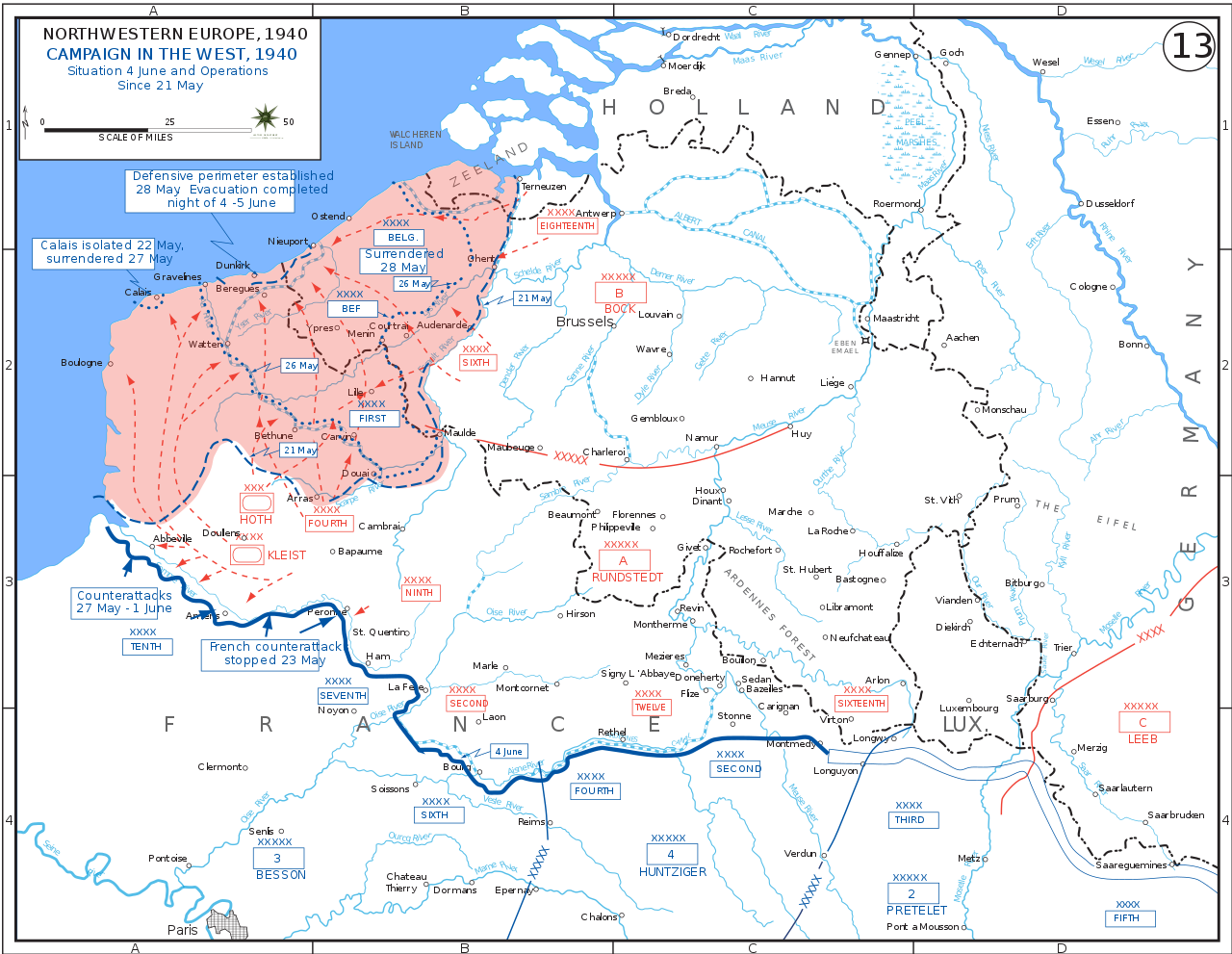
14-22 Jun, 1940: Germany captures Paris after sweeping around the Maginot Line, the French defensive position stretching from Switzerland to Belgium, splitting France into a German occupied coastal region and a collaborative regime in the South (Vichy France).-War by NatGeo.
Jun, 1940: Italy under Mussolini invades Greece and Egypt.-War by NatGeo.
Apr- May, 1940: Germany launches blitzkriegs through Denmark, Norway, Belgium, Netherlands, Luxembourg, and France.-War by NatGeo.
3 Sep, 1939: Britain and France declare war on Germany.-War by NatGeo.
1 Sep, 1939: Germany invades Poland igniting WWII (the USSR secretly invades E. Poland). The invasion of Poland showcases the German Blitzkrieg (lightning war)- using aircraft support, motorized divisions, columns of Panzer tanks, and 1.5M troops, Germany quickly cuts through Polish lines.-War by NatGeo.
Aug, 1939: Hitler signs a non-aggression pact with the USSR. A secret clause in the pact is the combined invasion of Poland, Germany to the West and USSR to the East, with both nations taking their half.-War by NatGeo.
Sep, 1938: Germany annexes Czechoslovakia.-War by NatGeo.
12 Mar, 1938: Germany annexes Austria.-War by NatGeo.
30 Jan, 1933: Adolf Hitler is appointed chancellor of Germany.-War by NatGeo.
__________________________________________________________________________________
WWII: The World Divided- Pacific
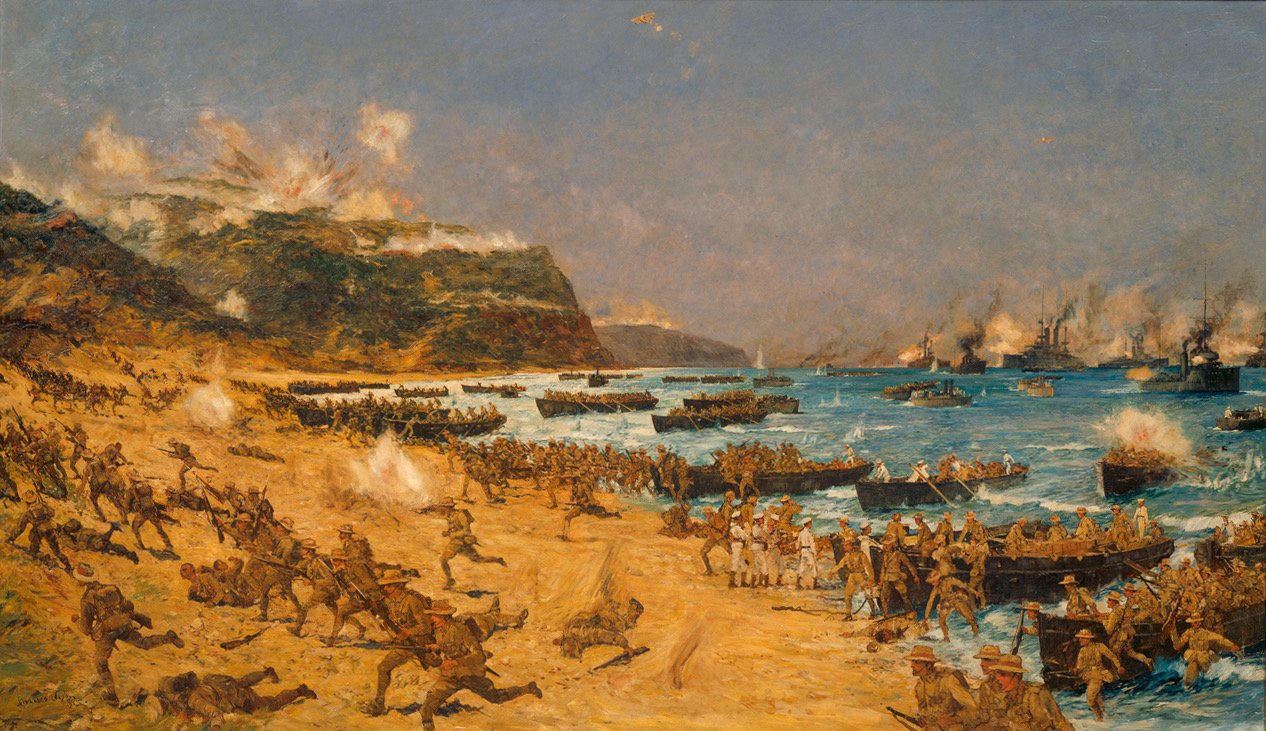
2 Sep, 1945: Japan formally surrenders ending WWII.-War by NatGeo.
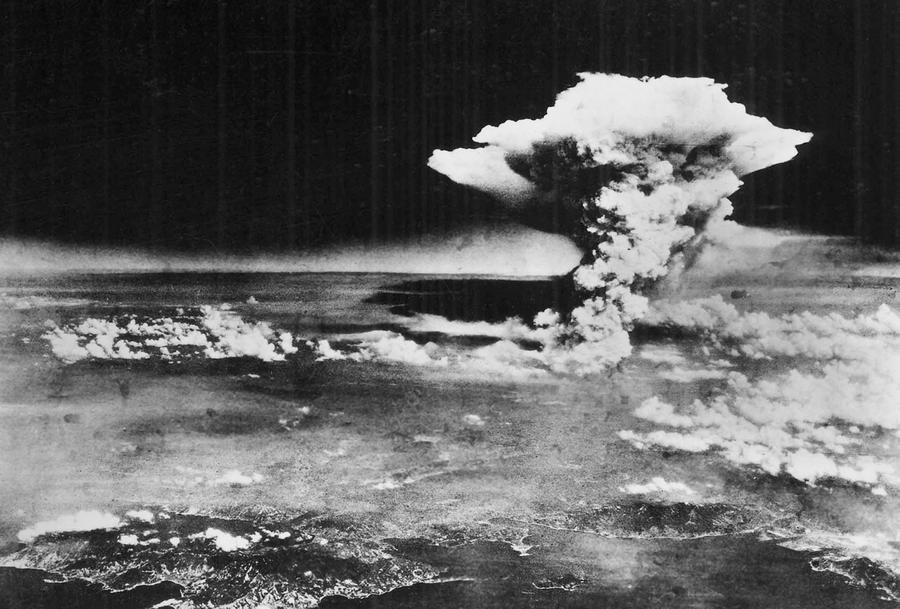
9 Aug, 1945: The US Army Air Force drops Fat Man, an implosion type fission bomb, on Nagasaki, Japan.-War by NatGeo.
6 Aug, 1945: The US Army Air Force drops Little Boy, a gun-type fission bomb, on Hiroshima, Japan.-War by NatGeo.
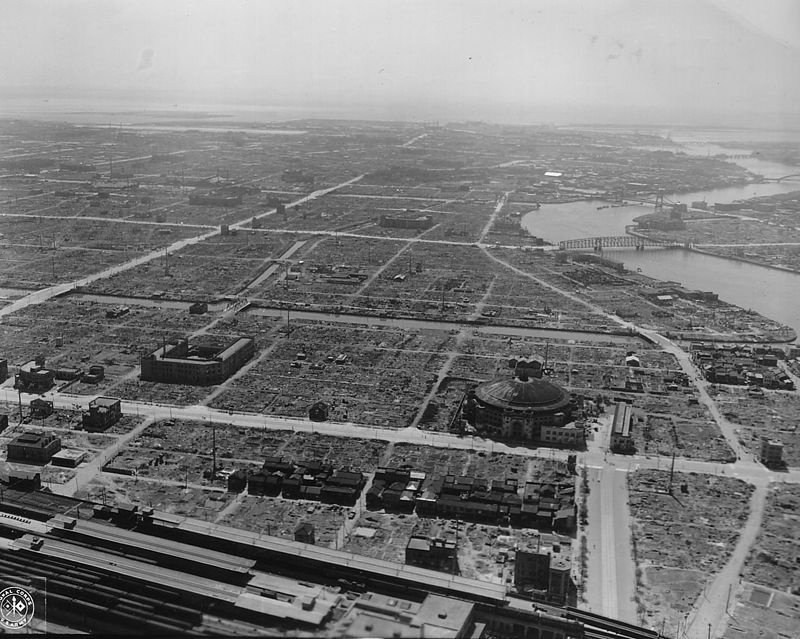
9-10 Mar, 1945: The US firebombing of Tokyo kills ~80,000 people.-War by NatGeo.
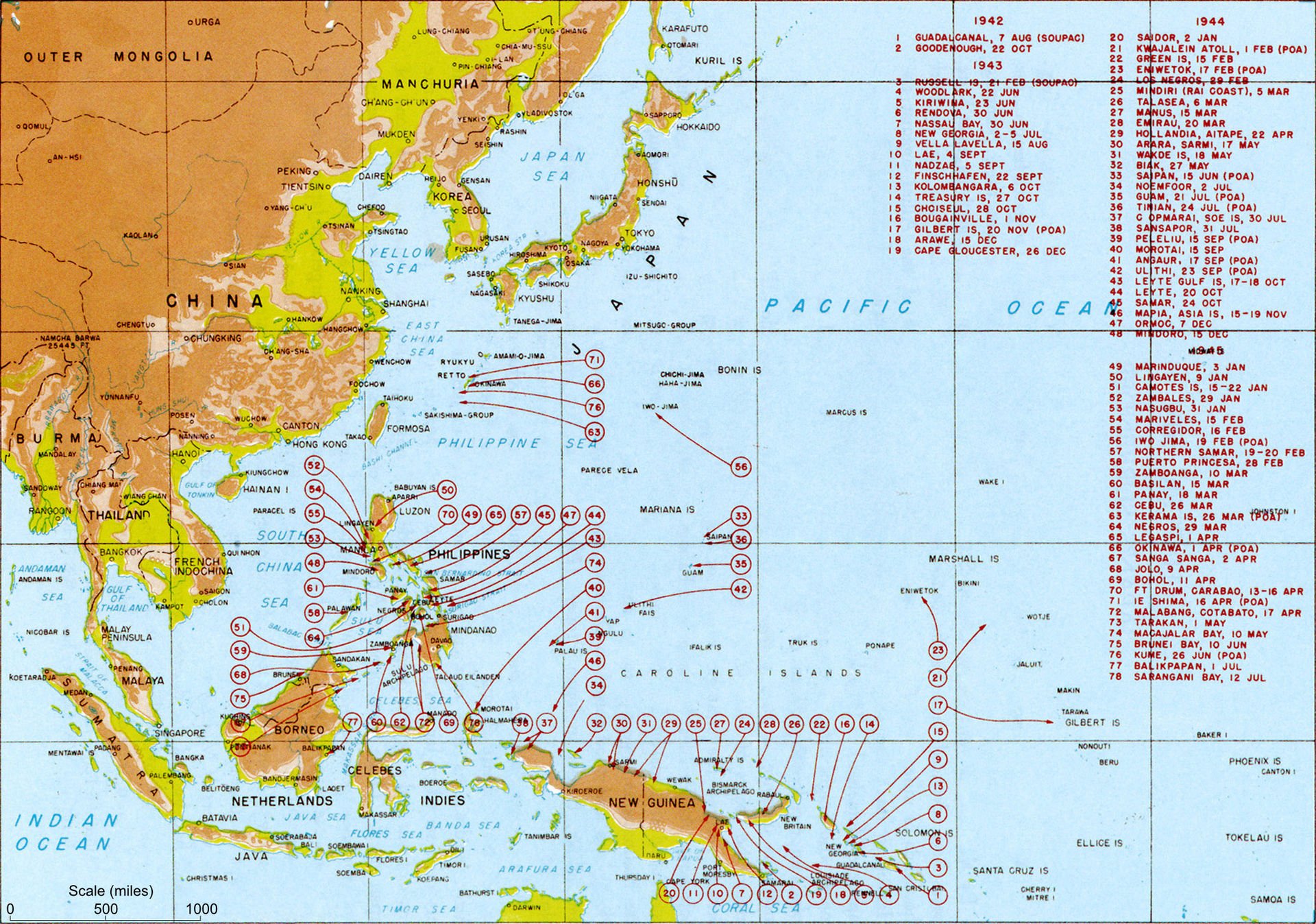
23-26 Oct, 1944: The Battle of Leyte Gulf, the largest naval battle in history. The US retakes the Philippines, the Japanese lose 26 warships and 20,000 soldiers and sailors, to the US’ 7 warships.-War by NatGeo.
Aug, 1942- Feb, 1943: The Battle of Guadalcanal; the US and allied forces defeat Japanese forces.-War by NatGeo.
3-7 Jun, 1942: The Battle of Midway; US forces defeat Japanese forces.-War by NatGeo.
15 Feb, 1942: Surender of the to the Japanese at Singapore.-War by NatGeo.
11 Dec, 1941: Japan’s allies, Germany & Italy, declare war on the USA.-War by NatGeo.
8 Dec, 1941: The USA declares war on Japan.-War by NatGeo.
7/8 Dec, 1941: Japan launches coordinated surprise attacks throughout the Pacific Ocean.-War by NatGeo.
8 Dec, 1941: Japan quickly takes Hong Kong, Guam, Wake Island, and the Philippines.-War by NatGeo.
7 Dec, 1941: “A Day Which Will Live in Infamy,” Japan conducts a surprise attack on the US Naval Base at Pearl Harbor, Oahu. Two waves of ~360 Japanese aircraft bomb and strafe US airfields and ships at anchor, destroying 180 aircraft, damaging all battleships and sinking two and killing more than 2400 servicemen.-War by NatGeo.
__________________________________________________________________________________
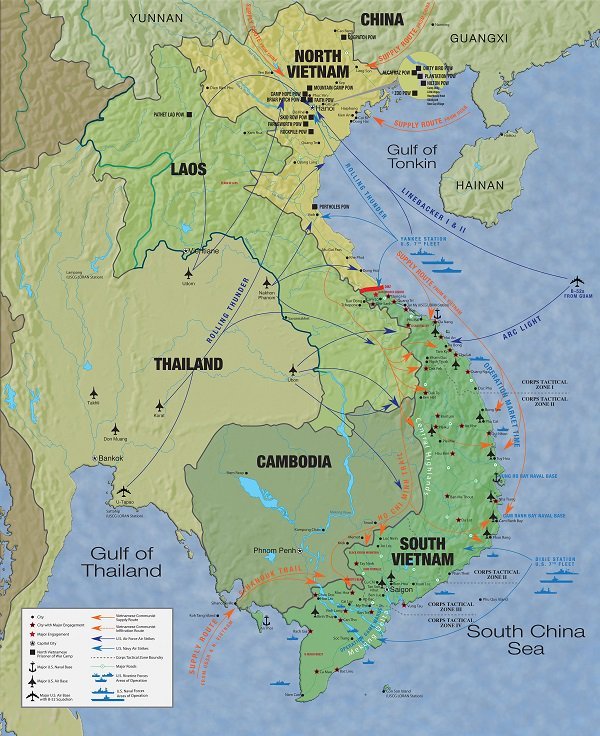
Vietnam: An Undeclared War
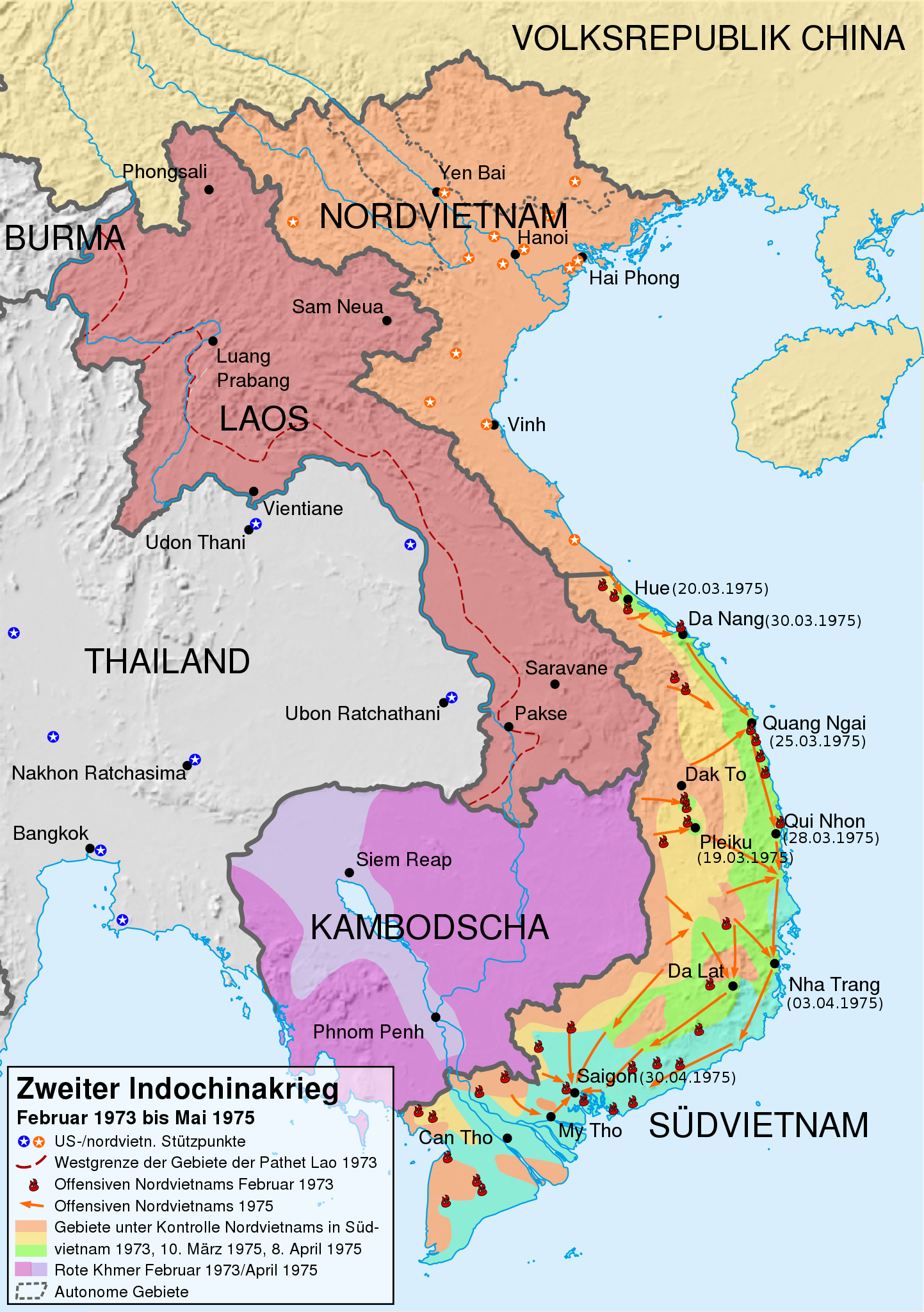
30 Apr, 1975: North Vietnamese forces invade Saigon; the last remaining Americans flee Saigon as North Vietnamese troops approach the city.-War by NatGeo.
27 Jan, 1973: The Treaty of Paris is signed by the US, N. Vietnam, S. Vietnam, and Viet Cong; the US agrees to withdraw troops within 60 days. In all, ~58,000 American, >1M Vietnamese fighters, and ~2M civilians had died in the conflict.-War by NatGeo.
1969-1970: The US conducts strategic bombing in Laos & Cambodia.-War by NatGeo.
13-20 May, 1969: The Battle of Hamburger Hill; US and ARVN forces defeat PAVN forces on Hill 937, a ridge on the mountain Dong Ap Bia in Central Vietnam (Wiki).
31 Jan- 2 Mar, 1968: The Battle of Hue; US and ARVN forces defeat PAVN forces while recapturing Hue (Wiki).
30 Jan, 1968: The Tet Offensive; a coordinated attack against dozens of targets in South Vietnam including the US Embassy in Saigon is launched by North Vietnamese and Viet Cong forces.-War by NatGeo.
21 Jan- 9 Jul, 1968: The Battle of Khe Sanh; PAVN forces begin a massive artillery bombardment of Khe Sanh, hitting the bases main store of ammunition and destroying 90% of its artillery and mortar rounds. For the next 77 days, US and S. Vietnamese forces fought off a massive N. Vietnamese siege. Some 10K PAVN soldiers are killed to ~500 USMC.-War by NatGeo.
14-17 Nov, 1965: Battle of la Drang Valley; US First Cavalry Div. and Soldiers of North Vietnam’s People’s Army of Vietnam (PAVN) fight a fierce battle in South Vietnam’s Central Highlands. 300 US and more than a 1000 North Vietnamese are killed.-War by NatGeo.
5 Aug, 1964: The Gulf of Tonkin Resolution is passed by the USG following a reported attack on US ships in the Gulf of Tonkin, authorizing military force in Vietnam.-War by NatGeo.
1960’s: US President JFK deploys US Military advisors to support the S. Vietnamese fight against pro-communist guerillas.-War by NatGeo.
21 Jul, 1954: The Geneva Accords temporarily divide Vietnam into North and South along the 17th parallel with the intent of reunification following the 1956 democratic elections. A liberation group known as the National Liberation Front (later called the Viet Cong) begins growing within South Vietnam.-War by NatGeo.
__________________________________________________________________________________
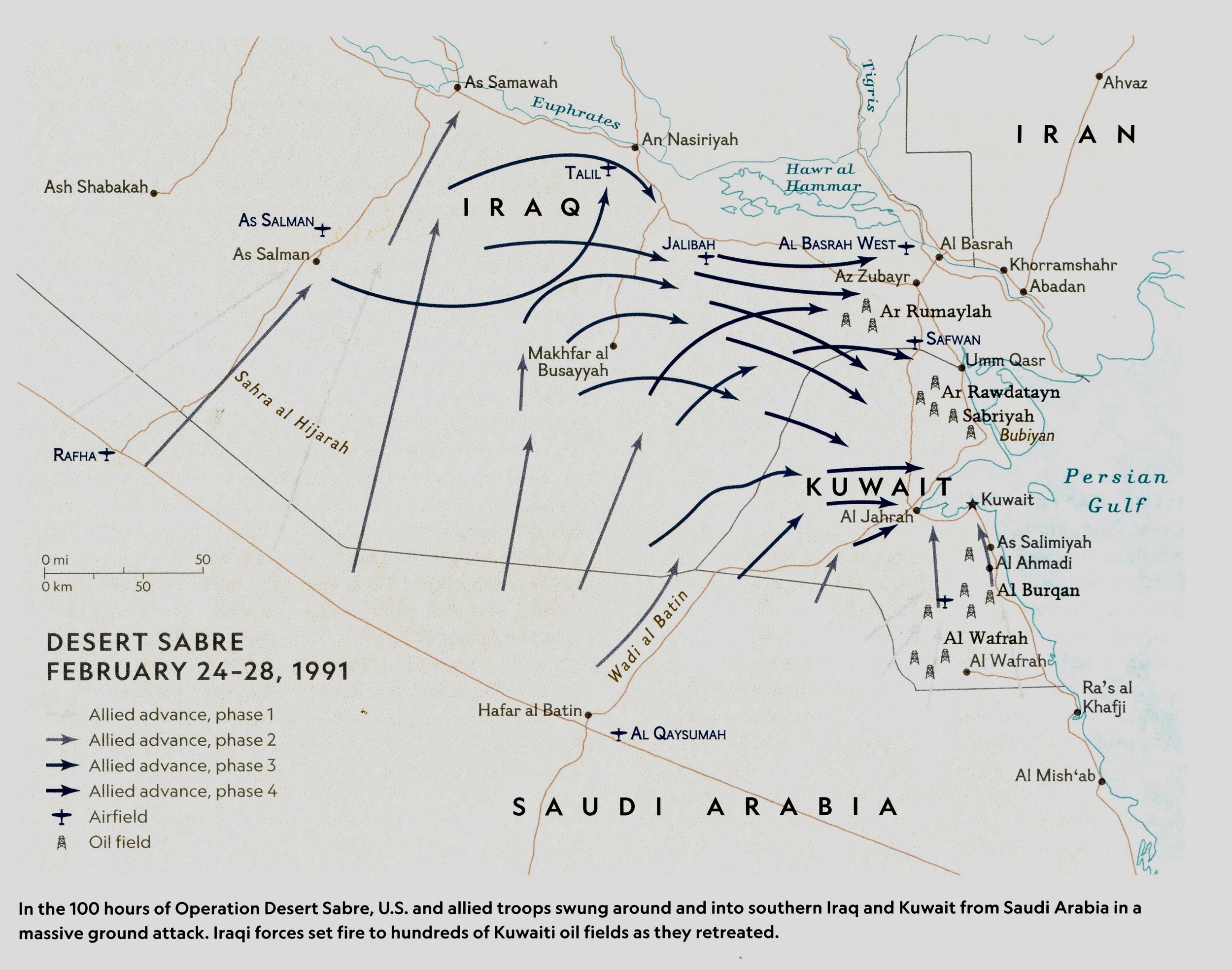
Desert Shield & Desert Storm
3 Mar, 1991: Hostilities end after a Ceasefire is negotiated between Allied and Iraqi Forces.-War by NatGeo.
Feb, 1991: Retreating Iraqi forces set fire to more than 600 oil wells in Kuwait.-War by NatGeo.
17 Jan- 28 Feb, 1991: Operation Desert Storm to liberate Kuwait begins with massive air attacks on targets in Kuwait and Iraq. Iraqi leader Saddam Hussein responds by launching Scud Missiles at allied targets and Israel. The Coalition loses ~300 to some 10,000 Iraqi soldiers.-War by NatGeo.
24-28 Feb, 1991: Desert Storm Ground Combat Phase.-War by NatGeo.
26 Feb, 1991: US, French, and Arab combat troops enter Kuwait City.-War by NatGeo.
17 Jan- 24 Feb, 1991: Desert Storms Air Combat Phase.-War by NatGeo.
17-18 Jan, 1991: Operation Senior Surprise (aka Secret Squirrel); 7x B-52s flew 22,500km nonstop for more than 35 hours from Louisiana to Iraq and back, refueling midflight, to launch GPS-guided cruise missiles toward Iraqi targets.-War by NatGeo.
29 Nov, 1990: The UNSC authorizes action against Iraq if it does not withdraw from Kuwait by 15 Jan, 1991.-War by NatGeo.
2 Aug, 1990: Iraqi troops invade Kuwait seeking to add the small countries vast oil reserves to their own.-War by NatGeo.
__________________________________________________________________________________
People
Jean Baptiste Vaquette de Gribeuval: French Engineer who made Mobile Artillery. As French inspector-general of artillery, Gribeauval redesigned and standardized the guns, reducing their weight and providing them with sturdy carriages that could easily be pulled by a pair of draft horses.
__________________________________________________________________________________
Terminology
Bushido: The way of the warrior; stoicism, fearlessness, honor, and supreme loyalty to the commander, requiring prowess with sword, bow, and horse.
Daimyo: Local Japanese Warlords.
Samurai: “Those who Serve,” the Elite Warriors of the Daimyo.
Decimation: The Execution of one out of every ten soldiers in a misbehaving unit.
Europe’s Armed Knights: Wealthy nobles who could afford horses, armor, weapons, and their own infantry.
Grande Armée: The French Military built on conscription and led by experienced officers with men organized into infantry, cavalry, heavy cavalry, and dragoons, with mobile artillery. Supply trains were kept small to ensure the Army’s speed.
Lebensraum (Living Space): Hitler’s Ideology that Aryan’s deserved living space carved out of Slavic states to Germany’s East.
Macedonian Army: A mix of skilled calvary and a heavy Phalanx, 16 ranks deep and armed with 4m spears called Sarissas. The troops trained rigorously and traveled up to 24 km per day.
Operation Desert Shield: The buildup of defensive forces in Saudi Arabia.
Roman Army: Armed with 2m Javelins and heavy swords and protected by helmet, shield, breastplate, the legionnaires attack line by line, hurling the Javelins and following up with their blades. The strongest fighters, the veterans, brought up the rear.
Shogun: Military Dictator.
Tenochtitlan: The Aztecan capital built on an island in Lake Texcoco.
Triple Alliance (WWI Central Powers): Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy.
Triple Entente (WWI Allies): Britain, France, and Russia.
Yamashita Standard: A legal precedent that says a commander is responsible for crimes committed by his troops. Shortly after Japan surrendered, a US Military commission brought Yamashita to trial for war crimes, charging that his troops had committed atrocities against US soldiers in the islands. Although the crimes were carried out without his knowledge or approval, Yamashita was convicted and hanged in 1946.
__________________________________________________________________________________
Chronology
2015: The US DOD opens all combat roles to women.-Atlas of War by NatGeo.
1993: The USN and USAF open the combat flight community to women.-Atlas of War by NatGeo.
1939-1945: WWII is fought by almost 30 countries. The death toll is ~15M KIA and perhaps 45M civilian deaths.-Atlas of War by NatGeo.
~1470: Invention of the Harquebus, a long-barreled match lock weapon.-Atlas of War by NatGeo.
208: The Battle of Red Cliffs (aka the Battle of Chibi); a decisive naval battle fought between the allied forces of the southern Chinese warlords Sun Quan, Liu Bei, and Liu Qi, against the numerically superior forces of the northern warlord Cao Cao. The allied victory against Cao Cao gave the warlords control of the Yangtze and provided a line of defence that was the basis for a north-south axis of hostility.-Atlas of War by NatGeo.
__________________________________________________________________________________