The Lean Startup by Ries
Ref: Ries (2011). The Lean Startup. Penguin.
________________________________________________________
Summary
The Fundamentals and Lessons Learned with Business and LCC Startups.
Total manufacturing output in the United States is increasing (by 15% in the last decade) even as jobs continue to be lost. In effect, the huge productivity increases made possible by modern management and technology have created more productive capacity than firms know what to do with.
________________________________________________________
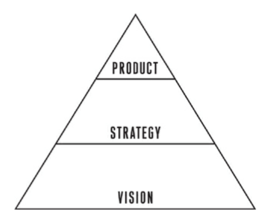
Start-Ups
The fundamental activity of a startup is to turn ideas into products, measure how customers respond, and then learn whether to pivot or persevere.
A comprehensive theory of entrepreneurship should address all the functions of an early-stage venture: vision and concept, product development, marketing and sales, scaling up, partnerships and distribution, and structure and organizational design. It has to provide a method for measuring progress in the context of extreme uncertainty.
The goal of a startup is to figure out the right thing to build—the thing customers want and will pay for—as quickly as possible.
Quantitative targets create the motivation to engage in qualitative inquiry.
________________________________________________________