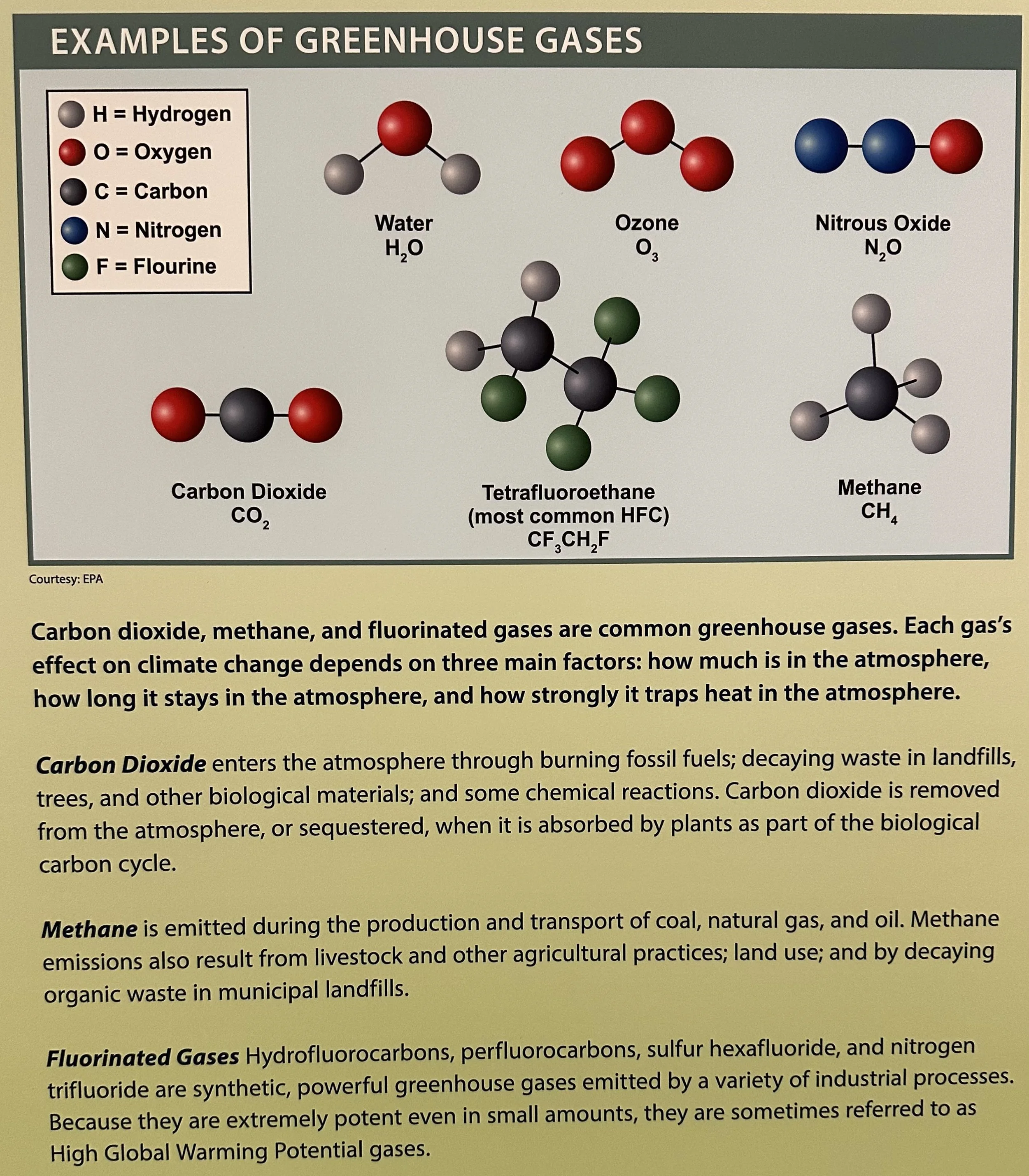
Environmental Protection Agency Museum
Ref: EPA. EPA Museum. Washington DC.
___________________________________________________________________________
EPA’s Lines of Effort
Land: Technology investments, respond to emergencies, Revitalize Communities, Environmental Justice, Sustainable Practices, Tribal Partnerships, Worker Protections, Prudent Pesticide Use, Productive Farms, Healthy Animals, Safer Chemicals, Create New Jobs, Food Recovery, Protect Bees, Green Spaces, Clean Up Land, Reduce Waste, Superfund.
Water: Protect Groundwater, Hurricane Response, Manage Wastewater, Plastic-Free Waters, Conserve Coral Reefs, Storm Preparedness, Safe Drinking Water, Flood Protection, Vibrant Ecosystems, Wildlife Habitat, Joyful Recreation, Use Water Wisely, Protect Wetlands, Bountiful Bays, Healthy Fish, Clean Beaches, Water Jobs, Clean Oceans.
Air: Enhanced Research, Particulates Matter, Changing Climate, Indoor Air Quality, Asthma Awareness, Children's Health, Healthy Schools, Radon Testing, Electric Vehicles, Renewable Fuels, Energy Savings, Smart Growth, Breathe Easy, More Trees, Green Power, Sun Safety, Energy Star, Clear Skies.
___________________________________________________________________________
Chronology
2021: POTUS Biden forms the first ever National Climate Task Force to mobilize every USG agency to prioritize acting on climate change (EPA Museum).
2020: POTUS Trump signs the American Innovation and Manufacturing (AIM) Act into law to facilitate the transition to more climate-friendly technologies. The AIM Act limits the amount of hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs)- potent GHGs used in refrigeration, AC, and other sectors-that companies can produce or import. The goal is an 85% reduction in the production and consumption of HFCs in the USA by 2036 (EPA Museum).
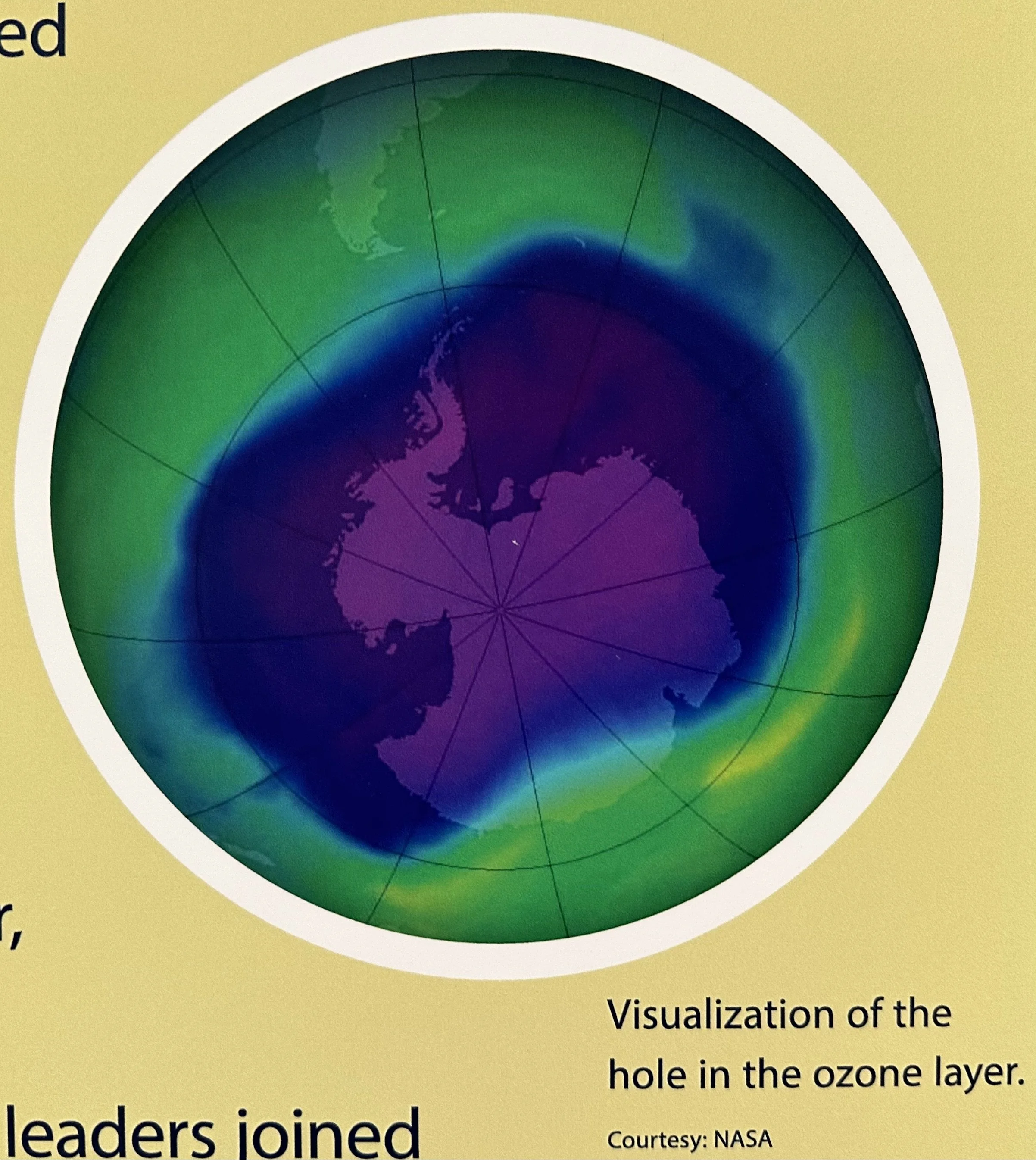
1987: POTUS Reagan and world leaders join the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer. By 1996 CFCs had been almost completely eliminated worldwide (EPA Museum).
1985: Scientists discover a thinning in the ozone layer (EPA Museum).
1974: Scientists determine that chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), which were used widely in AC, refrigeration, and aerosol sprays, could break down the ozone layer (EPA Museum).
___________________________________________________________________________