Fighting Disease by Michaud & Feinstein
Ref: Michaud & Feinstein (1989). Fighting Disease: The Complete Guide to Natural Immune Power. Rodale Publishing.
___________________________________________________________
Summary
The function of the immune system and how it fights off antigens.
___________________________________________________________
Immune System
Leukocytes: White Blood Cells (WBCs)
80% Phagocytes (Neutrophil and Macrophages).
20% Lymphocytes (B-Cells, T-Cells).
Non- Specialized (Phagocytes)
Neutrophils (Shock Cells): Comprise 60-75% of WBCs. They are the first to move to a wound to engage antigens; pus at the site of a wound is comprised of dead neutrophils.
Macrophage: Large WBCs that engulf antigens whole.
NK Cells: Fight off cells that have gone bad- tumor cells.
Specialized (Lymphocytes)
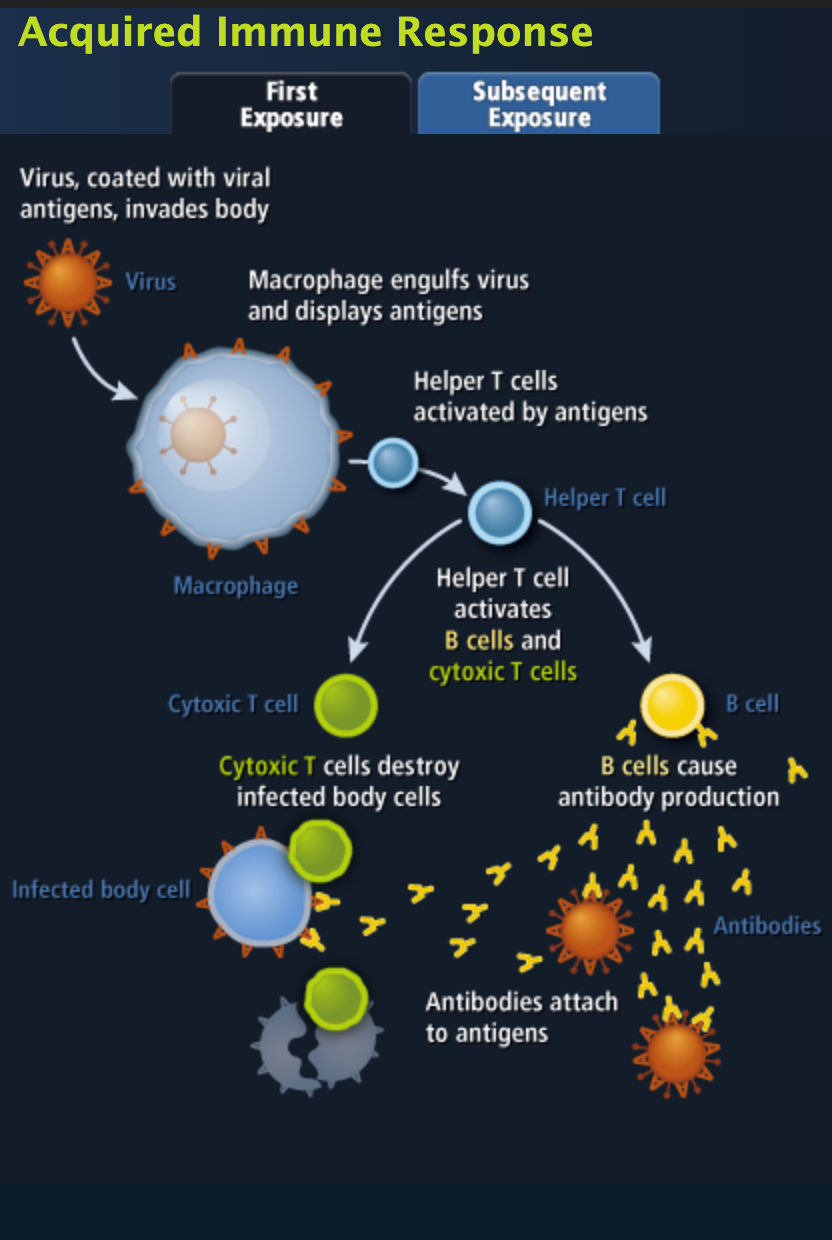
T-Cells: Live in the Thymus; they perforate the cell membrane of antigen protein coats, which shuts down the viral DNA copying. Some T-Cells watch the battle and make decisions while other T-Cells clone and fight, those that survive watch for the virus again and know how to respond. These cells patrol the body and search for any cell/organism without a protein code that is unique only to the self. T-Cells tell the immune system when to respond and how to respond.
B-Cells: Grow in Bone Marrow; they turn into plasma cells and create antibodies which inactivate antigens. Plasma cells can clone themselves and call in more macrophages and lymphocytes.
Immunodeficiency: loss of some or all of the immune system functions.
Auto-Immune Disease: When your cells attack your own body.
Bone Marrow: Produce Stem Cells
Mast Cells: Release Histamine; sneeze, runny nose, hives (urticaria).
___________________________________________________________
Pathogens
Pathogens: Bacteria, Viruses, Yeasts, Fungi, Parasites that invade a host and are regarded as a threat by the immune system and capable of stimulating an immune response.
Bacteria: Sits outside body cells and secretes toxins.
Virus: Removes protein coat to slip into nucleus of a cell and copy its DNA, when the cell dies, thousands of new viruses come out.
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV): attacks helper T-Cells and clones itself.
Antigens: Proteins found on the surface of the pathogen.
___________________________________________________________
Endocrine System
Hormones: Chemical messengers that relay instructions from endocrine glands to the body.
Interleukin: Hormones that carry messengers from one immune system cell to another.
IL-1: Macrophage that has devoured an antigen invader. Brings on fever and induces fatigue.
___________________________________________________________